Assessment and Management of Anti-Insulin Autoantibodies in Varying Presentations of Insulin Autoimmune Syndrome
- PMID: 30085133
- PMCID: PMC6179165
- DOI: 10.1210/jc.2018-00972
Assessment and Management of Anti-Insulin Autoantibodies in Varying Presentations of Insulin Autoimmune Syndrome
Abstract
Context: Insulin autoimmune syndrome (IAS), spontaneous hyperinsulinemic hypoglycemia due to insulin-binding autoantibodies, may be difficult to distinguish from tumoral or other forms of hyperinsulinemic hypoglycemia, including surreptitious insulin administration. No standardized treatment regimen exists.
Objectives: To evaluate an analytic approach to IAS and responses to different treatments.
Design and setting: Observational study in the UK Severe Insulin Resistance Service.
Patients: Six patients with hyperinsulinemic hypoglycemia and detectable circulating anti-insulin antibody (IA).
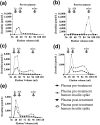
Main outcome measures: Glycemia, plasma insulin, and C-peptide concentrations by immunoassay or mass spectrometry (MS). Immunoreactive insulin was determined in the context of polyethylene glycol (PEG) precipitation and gel filtration chromatography (GFC). IA quantification using ELISA and RIA, and IA were further characterized using radioligand binding studies.
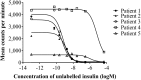
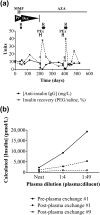
Results: All patients were diagnosed with IAS (five IgG, one IgA) based on a high insulin/C-peptide ratio, low insulin recovery after PEG precipitation, and GFC evidence of antibody-bound insulin. Neither ELISA nor RIA result proved diagnostic for every case. MS provided a more robust quantification of insulin in the context of IA. One patient was managed conservatively, four were treated with diazoxide without sustained benefit, and four were treated with immunosuppression with highly variable responses. IA affinity did not appear to influence presentation or prognosis.
Conclusions: IAS should be considered in patients with hyperinsulinemic hypoglycemia and a high insulin/C-peptide ratio. Low insulin recovery on PEG precipitation supports the presence of insulin-binding antibodies, with GFC providing definitive confirmation. Immunomodulatory therapy should be customized according to individual needs and clinical response.
Figures

References
-
- Uchigata Y, Eguchi Y, Takayama-Hasumi S, Omori Y. Insulin autoimmune syndrome (Hirata disease): clinical features and epidemiology in Japan. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 1994;22(2–3):89–94. - PubMed
-
- Takayama-Hasumi S, Eguchi Y, Sato A, Morita C, Hirata Y. Insulin autoimmune syndrome is the third leading cause of spontaneous hypoglycemic attacks in Japan. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 1990;10(3):211–214. - PubMed
-
- Cryer PE, Axelrod L, Grossman AB, Heller SR, Montori VM, Seaquist ER, Service FJ; Endocrine Society . Evaluation and management of adult hypoglycemic disorders: an Endocrine Society Clinical Practice Guideline. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2009;94(3):709–728. - PubMed
-
- Lebowitz MR, Blumenthal SA. The molar ratio of insulin to C-peptide: an aid to the diagnosis of hypoglycemia due to surreptitious (or inadvertent) insulin administration. Arch Intern Med. 1993;153(5):650–655. - PubMed
-
- Schlosser M, Mueller PW, Törn C, Bonifacio E, Bingley PJ; Participating Laboratories . Diabetes Antibody Standardization Program: evaluation of assays for insulin autoantibodies. Diabetologia. 2010;53(12):2611–2620. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- MC_UU_12012/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- MC_UU_12012/3/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- MC_UU_00014/5/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- MC_UU_12012/5/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- 106 263/Z/14/Z/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- 106262/Z/14/Z/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- 210752/Z/18/Z/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- MC_UU_00014/3/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- MR/M009041/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- MR/M024873/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

