Stereotactic Body Radiation Therapy for Biopsy-Proven Primary Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer: Experience of Patients With Inoperable Cancer at a Single Brazilian Institution
- PMID: 30085881
- PMCID: PMC6223518
- DOI: 10.1200/JGO.18.00020
Stereotactic Body Radiation Therapy for Biopsy-Proven Primary Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer: Experience of Patients With Inoperable Cancer at a Single Brazilian Institution
Abstract
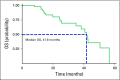
Purpose Stereotactic body radiation therapy (SBRT) has emerged as a treatment option for patients with non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC). We report the clinical outcomes and toxicity for patients with inoperable primary NSCLC treated with SBRT. Methods Between 2007 and 2015, 102 consecutive lung lesions were treated with SBRT at our center, of which 59 primary NSCLC lesions (from 54 patients with inoperable disease) were retrospectively reviewed (43 lesions were excluded because of metastases or because there was no biopsy specimen). We report infield local control (LC) per SBRT target, regional or distant failure-free survival, and overall survival (OS) per patient, using Kaplan-Meier estimates. Serious toxicity was retrospectively scored using Common Terminology Criteria for Adverse Events, version 4. Results Most of the 54 patients were men (n = 41; 76%), median age was 75 years; stage IA (n = 36; 66%) and adenocarcinoma (n = 43; 80%) were the most common stage and histologic diagnosis, respectively. Five patients had two lung lesions. A median of three fractions (range, 3 to 5 fractions) and a total median dose of 54 Gy (range, 45 to 60 Gy) per lesion were prescribed. The median follow-up was 17.8 months (range, 4 to 56.4 months). The 2-year rates of LC, regional or distant failure-free survival, and OS were 89.1% (95% CI, 72.2% to 96%), 79% (95% CI, 59.8% to 89.8%), and 80% (95% CI, 64% to 89.8%), respectively. Grade 3 to 4 toxicities were observed in two patients (3%): grade 3 pneumonitis (n = 1) and grade 4 skin toxicity (n = 1). Conclusion SBRT results in high rates of 2-year LC, regional or distant failure-free survival, and OS with low rates of severe toxicity in patients with inoperable primary NSCLC disease.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Lung stereotactic body radiation therapy for elderly patients aged ≥ 80 years with pathologically proven early-stage non-small cell lung cancer: a retrospective cohort study.Radiat Oncol. 2021 Feb 23;16(1):39. doi: 10.1186/s13014-021-01769-7. Radiat Oncol. 2021. PMID: 33622369 Free PMC article.
-
Stereotactic body radiation therapy (SBRT) improves local control and overall survival compared to conventionally fractionated radiation for stage I non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC).Acta Oncol. 2018 Nov;57(11):1567-1573. doi: 10.1080/0284186X.2018.1481292. Epub 2018 Jun 6. Acta Oncol. 2018. PMID: 29873277 Free PMC article.
-
Stereotactic Body Radiation Therapy for Stage I Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: A Retrospective, Single-Center Study of 55 Patients.Oncology. 2016;91(4):194-204. doi: 10.1159/000447540. Epub 2016 Jul 19. Oncology. 2016. PMID: 27427761
-
Risk-adapted robotic stereotactic body radiation therapy for inoperable early-stage non-small-cell lung cancer.Strahlenther Onkol. 2018 Feb;194(2):91-97. doi: 10.1007/s00066-017-1194-x. Epub 2017 Aug 15. Strahlenther Onkol. 2018. PMID: 28812120 Review. English.
-
Local Control After Stereotactic Body Radiation Therapy for Stage I Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer.Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2021 May 1;110(1):160-171. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2019.03.045. Epub 2019 Apr 5. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2021. PMID: 30954520 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Local control and survival after stereotactic body radiation therapy of early-stage lung cancer patients in Slovenia.Radiol Oncol. 2023 Jul 26;57(3):389-396. doi: 10.2478/raon-2023-0032. eCollection 2023 Sep 1. Radiol Oncol. 2023. PMID: 37494591 Free PMC article.
-
Response evaluation after stereotactic ablative radiotherapy for localised non-small-cell lung cancer: an equipoise of available resource and accuracy.Br J Radiol. 2020 Feb 1;93(1106):20190647. doi: 10.1259/bjr.20190647. Epub 2019 Dec 11. Br J Radiol. 2020. PMID: 31778312 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of stereotactic body radiotherapy and radiofrequency ablation for early-stage non-small cell lung cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Ann Transl Med. 2022 Jan;10(2):104. doi: 10.21037/atm-21-6256. Ann Transl Med. 2022. PMID: 35282118 Free PMC article.
-
Real-World Evidence of Health Outcomes Related to Lung Stereotactic Body Radiation Therapy in Brazil.JCO Glob Oncol. 2022 Nov;8:e2200061. doi: 10.1200/GO.22.00061. JCO Glob Oncol. 2022. PMID: 36351211 Free PMC article.
-
Applying PET-CT for predicting the efficacy of SBRT to inoperable early-stage lung adenocarcinoma: A Brazilian case-series.Lancet Reg Health Am. 2022 Mar 30;11:100241. doi: 10.1016/j.lana.2022.100241. eCollection 2022 Jul. Lancet Reg Health Am. 2022. PMID: 36778931 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Siegel RL, Miller KD, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2017. CA Cancer J Clin. 2017;67:7–30. - PubMed
-
- Naruke T, Tsuchiya R, Kondo H, et al. Prognosis and survival after resection for bronchogenic carcinoma based on the 1997 TNM-staging classification: The Japanese experience. Ann Thorac Surg. 2001;71:1759–1764. - PubMed
-
- Onishi H, Shirato H, Nagata Y, et al. Hypofractionated stereotactic radiotherapy (HypoFXSRT) for stage I non-small cell lung cancer: Updated results of 257 patients in a Japanese multi-institutional study. J Thorac Oncol. 2007;2(7) suppl 3:S94–S100. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical