Ongoing measles outbreak in Greece related to the recent European-wide epidemic
- PMID: 30086813
- PMCID: PMC9507959
- DOI: 10.1017/S0950268818002170
Ongoing measles outbreak in Greece related to the recent European-wide epidemic
Abstract
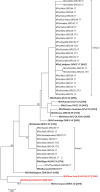
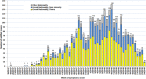
We report an ongoing measles outbreak in Greece. The first cases were notified through the mandatory notification system on May 2017 in Northern Greece and concerned a cluster of three imported cases in unvaccinated Roma siblings. So far, 3150 cases have been reported in all 13 Regions. Initially, the outbreak mainly affected Greek Roma but as it progressed it spread to non-minority Greek nationals. The outbreak reached its ultimate peak on week 10/2018 but from week 15/2018 has been gradually declining. Most cases (60.6%) were Roma (especially children <10 year-old) followed by non-minority Greek nationals (29.3%; mostly young adults). The majority (80.4%) were unvaccinated. Interestingly, 129 (4.1%) cases were healthcare workers (HCWs). Genotype B3 was identified by molecular methods in all 87 cases tested. Overall, 61.3% of the cases were hospitalised. Complications were reported in 17.1% of the cases among which four deaths. The outbreak occurred after 3 years without local endemic measles transmission. Extensive vaccination implemented as the major public health measure managed to prevent the emergence of a large number of cases in refugee/migrant hosting sites. Mitigation efforts currently focus on raising awareness among HCWs and closing the immunisation gap in populations with suboptimal vaccination coverage.
Keywords: Epidemiology; Greece; measles; outbreak.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures

References
-
- European Commission (2012) Commission Implementing Decision of 8 August 2012 amending Decision 2002/253/EC laying down case definitions for reporting communicable diseases to the Community network under Decision No 2119/98/EC of the European Parliament and of the Council. Luxembourg: Publications Office of the European Union. L262 27 September 2012. Available at http://eur-lex.europa.eu/legal-content/EN/TXT/?uri=OJ%3AL%3A2012%3A262%3... (Accessed 5 March 2018).
-
- World Health Organization (WHO) (2012) Global Measles and Rubella Strategic Plan 2012–2020. Geneva: WHO. Available at http://apps.who.int/iris/bitstream/10665/44855/1/9789241503396_eng.pdf (Accessed 5 March 2018).
-
- Pervanidou D et al. (2010) Spotlight on measles 2010: ongoing measles outbreak in Greece, January–July 2010. Euro Surveillance 15, pii=19629. - PubMed
-
- World Health Organization Regional Office for Europe (WHO/Europe) (2017) Fifth meeting of the European Regional Verification Commission for Measles and Rubella Elimination (RVC) 24–26 October 2016, Copenhagen, Denmark. Copenhagen: WHO/Europe. Available at http://www.euro.who.int/en/health-topics/communicable-diseases/measles-a... (Accessed 5 March 2018).
-
- World Health Organization Regional Office for Europe (WHO/Europe) (2017) Sixth meeting of the European Regional Verification Commission for Measles and Rubella Elimination (RVC) 15–17 June 2017, Bucharest, Romania. Copenhagen: WHO/Europe. Available at http://www.euro.who.int/en/health-topics/communicable-diseases/measles-a...) (Accessed 5 March 2018).
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

