Effects of the traditional Chinese medicine baicalein on the viability of random pattern skin flaps in rats
- PMID: 30087551
- PMCID: PMC6061754
- DOI: 10.2147/DDDT.S173371
Effects of the traditional Chinese medicine baicalein on the viability of random pattern skin flaps in rats
Abstract
Background: Random skin flaps are routinely placed during plastic and reconstructive surgery, but the distal areas often develop ischemia and necrosis. Baicalein, a major flavonoid extracted from the traditional Chinese herbal medicine huangqin, Scutellaria baicalensis Georgi, may improve flap viability.
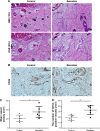
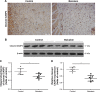
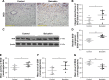
Materials and methods: Rats were randomly divided into baicalein and control groups and they underwent placement of modified McFarlane flaps after intraperitoneal administration of baicalein or vehicle. Flap survival and water content were measured 7 days later, as were angiogenesis, apoptosis, and oxidative stress in ischemic flaps.
Results: Baicalein promoted flap survival, reduced edema, increased mean vessel density, and enhanced vascular endothelial growth factor production at both the translational and transcriptional levels. Baicalein reduced caspase 3 cleavage, increased superoxidase dismutase and glutathione levels, and decreased the malondialdehyde level.
Conclusion: Baicalein promoted flap viability by stimulating angiogenesis and inhibiting apoptosis and oxidation.
Keywords: angiogenesis; apoptosis; baicalein; oxidation; random skin flap.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures


References
-
- Lee MS, Ahmad T, Lee J, et al. Dual delivery of growth factors with coacervate-coated poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid) nanofiber improves neovascularization ina mouse skin flap model. Biomaterials. 2017;124:65–77. - PubMed
-
- Deheng C, Kailiang Z, Weidong W, et al. Salidroside promotes random skin flap survival in rats by enhancing angiogenesis and inhibiting apoptosis. J Reconstr Microsurg. 2016;32(8):580–586. - PubMed
-
- Roh TS, Jung BK, Yun I, Lew DH, Kim YS. Effect of botulinum toxin A on vasoconstriction and sympathetic neurotransmitters in a murine random pattern skin flap model. Wound Repair Regen. 2017;25(1):75–85. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

