Olfactory Neurons and Brain Centers Directing Oviposition Decisions in Drosophila
- PMID: 30089274
- PMCID: PMC6290906
- DOI: 10.1016/j.celrep.2018.07.018
Olfactory Neurons and Brain Centers Directing Oviposition Decisions in Drosophila
Abstract
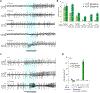
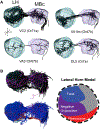
The sense of smell influences many behaviors, yet how odors are represented in the brain remains unclear. A major challenge to studying olfaction is the lack of methods allowing activation of specific types of olfactory neurons in an ethologically relevant setting. To address this, we developed a genetic method in Drosophila called olfactogenetics in which a narrowly tuned odorant receptor, Or56a, is ectopically expressed in different olfactory neuron types. Stimulation with geosmin (the only known Or56a ligand) in an Or56a mutant background leads to specific activation of only target olfactory neuron types. We used this approach to identify olfactory sensory neurons (OSNs) that directly guide oviposition decisions. We identify 5 OSN-types (Or71a, Or47b, Or49a, Or67b, and Or7a) that, when activated alone, suppress oviposition. Projection neurons partnering with these OSNs share a region of innervation in the lateral horn, suggesting that oviposition site selection might be encoded in this brain region.
Keywords: genetic technique; genetics; geosmin; odorant receptors; olfaction; olfactogenetics; olfactory; oviposition; projection neurons; vinegar fly.
Copyright © 2018 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
DECLARATION OF INTERESTS
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



References
-
- Andersson MN, Löfstedt C, and Newcomb RD (2015). Insect olfaction and the evolution of receptor Tuning. Front. Ecol. Evol 3, 1–53.
-
- Badel L, Ohta K, Tsuchimoto Y, and Kazama H (2016). Decoding of context-dependent olfactory behavior in Drosophila. Neuron 91, 155–167. - PubMed
-
- Barlow HB (1961). Possible principles underlying the transformations of sensory messages. In Sensory Communication, Rosenblith WA, ed. (MIT Press; ), pp. 217–234.
-
- Bartelt RJ, Schaner AM, and Jackson LL (1985). cis-Vaccenyl acetate as an aggregation pheromone inDrosophila melanogaster. J. Chem. Ecol 11, 1747–1756. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

