Hypoxia-inducible factor 2α: a novel target in gliomas
- PMID: 30089425
- PMCID: PMC6479274
- DOI: 10.4155/fmc-2018-0163
Hypoxia-inducible factor 2α: a novel target in gliomas
Abstract
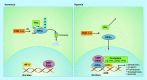
Hypoxia is an important contributor to aggressive behavior and resistance mechanisms in glioblastoma. Upregulation of hypoxia inducible transcription factors (HIFs) is the primary adaptive cellular response to a hypoxic environment. While HIF1α has been widely studied in cancer, HIF2α offers a potentially more specific and appealing target in glioblastoma given expression in glioma stem cells and not normal neural progenitors, activation in states of chronic hypoxia and expression that correlates with glioma patient survival. A first-in-class HIF2α inhibitor, PT2385, is in clinical trials for renal cell carcinoma, and provides the first opportunity to therapeutically target this important pathway in glioma biology.
Keywords: cancer; glioblastoma; hypoxia; hypoxia-inducible factors.
Conflict of interest statement
This work was supported by a Musella Foundation Grant (JJ Renfrow). Research reported in this publication was also supported by the National Cancer Institute's Cancer Center Support Grant award number P30CA012197 issued to the Wake Forest Baptist Comprehensive Cancer Center. The content is solely the responsibility of the authors and does not necessarily represent the official views of the National Cancer Institute. The authors have no other relevant affiliations or financial involvement with any organization or entity with a financial interest in or financial conflict with the subject matter or materials discussed in the manuscript apart from those disclosed.
No writing assistance was utilized in the production of this manuscript.
Figures
References
-
- Höckel M, Vaupel P. Tumor hypoxia: definitions and current clinical, biologic, and molecular aspects. J. Natl Cancer Inst. 2001;93(4):266–276. - PubMed
-
- Axelson H, Fredlund E, Ovenberger M, Landberg G, Pahlman S. Hypoxia-induced dedifferentiation of tumor cells – a mechanism behind heterogeneity and aggressiveness of solid tumors. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 2005;16:554–563. - PubMed
-
- Harris AL. Hypoxia – a key regulatory factor in tumour growth. Nat. Rev. Cancer. 2002;2(1):38–47. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
