β Cell dysfunction exists more than 5 years before type 1 diabetes diagnosis
- PMID: 30089716
- PMCID: PMC6129118
- DOI: 10.1172/jci.insight.120877
β Cell dysfunction exists more than 5 years before type 1 diabetes diagnosis
Abstract
Background: The duration and patterns of β cell dysfunction during type 1 diabetes (T1D) development have not been fully defined.
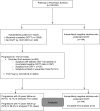
Methods: Metabolic measures derived from oral glucose tolerance tests (OGTTs) were compared between autoantibody-positive (aAb+) individuals followed in the TrialNet Pathway to Prevention study who developed diabetes after 5 or more years or less than 5 years of longitudinal follow-up (Progressors≥5, n = 75; Progressors<5, n = 474) and 144 aAb-negative (aAb-) relatives.
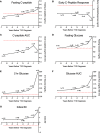
Results: Mean age at study entry was 15.0 ± 12.6 years for Progressors≥5; 12.0 ± 9.1 for Progressors<5; and 16.3 ± 10.4 for aAb- relatives. At baseline, Progressors≥5 already exhibited significantly lower fasting C-peptide (P < 0.01), C-peptide AUC (P < 0.001), and early C-peptide responses (30- to 0-minute C-peptide; P < 0.001) compared with aAb- relatives, while 2-hour glucose (P = 0.03), glucose AUC (<0.001), and Index60 (<0.001) were all higher. Despite significant baseline impairment, metabolic measures in Progressors≥5 were relatively stable until 2 years prior to T1D diagnosis, when there was accelerated C-peptide decline and rising glycemia from 2 years until diabetes diagnosis. Remarkably, patterns of progression within 3 years of diagnosis were nearly identical between Progressors≥5 and Progressors<5.
Conclusion: These data provide insight into the chronicity of β cell dysfunction in T1D and indicate that β cell dysfunction may precede diabetes diagnosis by more than 5 years in a subset of aAb+ individuals. Even among individuals with varying lengths of aAb positivity, our findings indicate that patterns of metabolic decline are uniform within the last 3 years of progression to T1D.
Trial registration: Clinicaltrials.gov NCT00097292.
Funding: The Type 1 Diabetes TrialNet Study Group is a clinical trials network currently funded by the NIH through the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases, the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases, and The Eunice Kennedy Shriver National Institute of Child Health and Human Development and the Juvenile Diabetes Research Foundation.
Keywords: Beta cells; Diabetes; Endocrinology; Insulin; Metabolism.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
- U01 DK085476/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UC4 DK104166/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK061010/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- I01 BX001733/BX/BLRD VA/United States
- P30 DK097512/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK103282/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK061042/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK085509/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UC4 DK117009/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK093954/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK017047/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK085466/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK103153/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK061058/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK106984/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK085499/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK107013/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK103266/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UC4 DK106993/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- K08 DK103983/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK107014/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK106994/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK061034/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK085461/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK103180/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK085465/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

