RNA velocity of single cells
- PMID: 30089906
- PMCID: PMC6130801
- DOI: 10.1038/s41586-018-0414-6
RNA velocity of single cells
Abstract
RNA abundance is a powerful indicator of the state of individual cells. Single-cell RNA sequencing can reveal RNA abundance with high quantitative accuracy, sensitivity and throughput1. However, this approach captures only a static snapshot at a point in time, posing a challenge for the analysis of time-resolved phenomena such as embryogenesis or tissue regeneration. Here we show that RNA velocity-the time derivative of the gene expression state-can be directly estimated by distinguishing between unspliced and spliced mRNAs in common single-cell RNA sequencing protocols. RNA velocity is a high-dimensional vector that predicts the future state of individual cells on a timescale of hours. We validate its accuracy in the neural crest lineage, demonstrate its use on multiple published datasets and technical platforms, reveal the branching lineage tree of the developing mouse hippocampus, and examine the kinetics of transcription in human embryonic brain. We expect RNA velocity to greatly aid the analysis of developmental lineages and cellular dynamics, particularly in humans.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
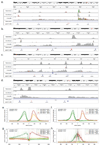


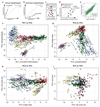


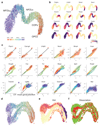

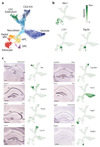
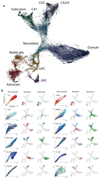


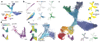
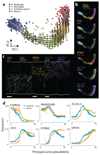
Comment in
-
Technique to measure the expression dynamics of each gene in a single cell.Nature. 2018 Aug;560(7719):434-435. doi: 10.1038/d41586-018-05882-8. Nature. 2018. PMID: 30127477 No abstract available.
-
Full speed ahead for single-cell analysis.Nat Rev Genet. 2018 Nov;19(11):668-669. doi: 10.1038/s41576-018-0049-3. Nat Rev Genet. 2018. PMID: 30154482 No abstract available.
-
RNA Velocity: Molecular Kinetics from Single-Cell RNA-Seq.Mol Cell. 2018 Oct 4;72(1):7-9. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2018.09.026. Mol Cell. 2018. PMID: 30290149
References
-
- Gaidatzis D, Burger L, Florescu M, Stadler MB. Analysis of intronic and exonic reads in RNA-seq data characterizes transcriptional and post-transcriptional regulation. Nat Biotechnol. 2015;33:722–729. - PubMed
-
- Picelli S, et al. Smart-seq2 for sensitive full-length transcriptome profiling in single cells. Nat Methods. 2013;10:1096–8. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

