Characterization and outcomes of local treatment for primary bladder lymphoma: A population-based cohort analysis
- PMID: 30089981
- PMCID: PMC6060605
- DOI: 10.4103/UA.UA_106_17
Characterization and outcomes of local treatment for primary bladder lymphoma: A population-based cohort analysis
Abstract
Introduction: Primary bladder lymphoma (PBL) is rare, representing 0.2% of extranodal lymphoma and less than 1% of all tumors originating in the bladder. Since the initial description of the disease, low-grade mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue (MALT) lymphoma has been reported as the most common subtype while high-grade disease was thought to represent only 20% of the reported cases.
Materials and methods: One hundred and ninety five patients with PBL from the Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results (SEER) registry from 1998-2010 were reviewed. Tumors were classified as high or low grade based on histologic subtype of lymphoma based on revised European-American Lymphoma classification system. Socio-demographic and clinical variables were reported, as well as survival outcome analyses using the Kaplan-Meier method and log-rank test. Cox proportional hazard analysis was used to generate hazard ratios for risk factors associated with mortality.
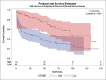
Results: Eighty-three patients (42.6%) with low-grade and 112 patients (57.4%) with high-grade bladder lymphoma were studied. There were no differences between the low and high-grade groups for socio-demographic or clinical variables. Median overall survival or patients with low-grade disease was 38 months versus 15 months for patients with high-grade disease (p< 0.001). Analysis demonstrated worse survival outcomes for patients with high-grade disease compared to low-grade disease (p< 0.001). On multivariable analysis, increasing age and high-grade disease were associated with worse disease specific mortality (p< 0.001).
Conclusion: Patient with high-grade primary bladder lymphoma had worse survival outcomes compared to those with low-grade disease. While transurethral resection provides tissue for diagnosis, immunotherapy/chemotherapy remains the mainstay of treatment for bladder lymphoma. Consolidation chemotherapy has been recommended in young patients not achieving complete remission with immunotherapy/chemotherapy.
Keywords: Bladder cancer; SEER; lymphoma; outcomes.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Kempton CL, Kurtin PJ, Inwards DJ, Wollan P, Bostwick DG. Malignant lymphoma of the bladder: Evidence from 36 cases that low-grade lymphoma of the MALT-type is the most common primary bladder lymphoma. Am J Surg Pathol. 1997;21:1324–33. - PubMed
-
- Mourad WA, Khalil S, Radwi A, Peracha A, Ezzat A. Primary T-cell lymphoma of the urinary bladder. Am J Surg Pathol. 1998;22:373–7. - PubMed
-
- Hughes M, Morrison A, Jackson R. Primary bladder lymphoma: Management and outcome of 12 patients with a review of the literature. Leuk Lymphoma. 2005;46:873–7. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources