Concentrated electrolytes stabilize bismuth-potassium batteries
- PMID: 30090306
- PMCID: PMC6062896
- DOI: 10.1039/c8sc01848k
Concentrated electrolytes stabilize bismuth-potassium batteries
Abstract
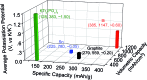
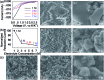
Storing as many as three K-ions per atom, bismuth is a promising anode material for rechargeable potassium-ion batteries that may replace lithium-ion batteries for large-scale electrical energy storage. However, Bi suffers from poor electrochemical cyclability in conventional electrolytes. Here, we demonstrate that a 5 molar (M) ether-based electrolyte, versus the typical 1 M electrolyte, can effectively passivate the bismuth surface due to elevated reduction resistance. This protection allows a bismuth-carbon anode to simultaneously achieve high specific capacity, electrochemical cyclability and Coulombic efficiency, as well as small potential hysteresis and improved rate capability. We show that at a high electrolyte concentration, the bismuth anode demonstrates excellent cyclability over 600 cycles with 85% capacity retention and an average Coulombic efficiency of 99.35% at 200 mA g-1. This "concentrated electrolyte" approach provides unexpected new insights to guide the development of long-cycle-life and high-safety potassium-ion batteries.
Figures





References
-
- Eftekhari A. J. Power Sources. 2004;126:221–228.
-
- Eftekhari A., Jian Z., Ji X. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces. 2017;9:4404–4419. - PubMed
-
- Jian Z., Luo W., Ji X. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2015;137:11566–11569. - PubMed
-
- Xue L., Li Y., Gao H., Zhou W., Lu X., Kaveevivitchai W., Manthiram A., Goodenough J. B. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2017;139:2164–2167. - PubMed
-
- Zhao Q., Wang J., Lu Y., Li Y., Liang G., Chen J. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2016;55:12528–12532. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

