Salvianolic acid B protects against doxorubicin induced cardiac dysfunction via inhibition of ER stress mediated cardiomyocyte apoptosis
- PMID: 30090438
- PMCID: PMC6062089
- DOI: 10.1039/c6tx00111d
Salvianolic acid B protects against doxorubicin induced cardiac dysfunction via inhibition of ER stress mediated cardiomyocyte apoptosis
Abstract
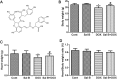
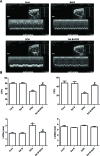
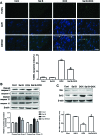
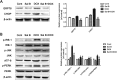
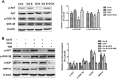
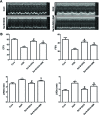
Salvia miltiorrhiza Bunge is a well-known medicinal plant in China. Salvianolic acid B (Sal B) is the most abundant bioactive compound extracted from the root of S. miltiorrhiza. The present study investigates the effect of Sal B on cardiac function and cardiomyocyte apoptosis in doxorubicin (DOX)-treated mice. After pretreatment with Sal B (2 mg kg-1 iv) for 7 d, male BALB/c mice were injected with a single dose of DOX (20 mg kg-1 ip). The cardioprotective effect of Sal B was observed on the 7th day after DOX treatment. DOX caused retarded body growth, apoptotic damage, and Bcl-2 expression disturbance. In contrast, Sal B pretreatment (2 mg kg-1 iv before DOX administration) attenuated the DOX induced apoptotic damage in heart tissues. Further study indicated that Sal B protected against DOX induced cardiotoxicity, at least, partially, by inhibiting endoplasmic reticulum stress, and by being involved in the PI3K/Akt pathway. These findings clarified the potential of Sal B as a promising reagent for treating DOX induced cardiotoxicity.
Figures

References
-
- Church R. J., McDuffie J. E., Sonee M., Otieno M., Ma J. Y., Liu X., Watkins P. B., Harrill A. H. Toxicol. Res. 2014;3:384–394.
-
- Yamanaka S., Tatsumi T., Shiraishi J., Mano A., Keira N., Matoba S., Asayama J., Fushiki S., Fliss H., Nakagawa M. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2003;41:870–878. - PubMed
-
- Jirkovská-Vávrová A., Roh J., Lenčová-Popelová O., Jirkovský E., Hrušková K., Potůčková-Macková E., Jansová H., Hašková P., Martinková P., Eisner T., Kratochvíl M., Šůs J., Macháček M., Vostatková-Tichotová L., Geršl V., Kalinowski D. S., Muller M. T., Richardson D. R., Vávrová K., Štěrba M., Šimůnek T. Toxicol. Res. 2015;4:1098–1114.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

