Imaging features of leadless cardiovascular devices
- PMID: 30091710
- PMCID: PMC6045516
- DOI: 10.5152/dir.2018.17462
Imaging features of leadless cardiovascular devices
Abstract
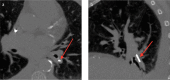
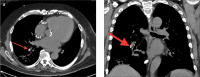
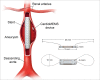
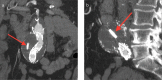
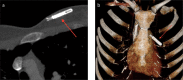
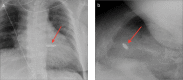
Cardiovascular devices and hemodynamic monitoring systems continue to evolve with the goal of allowing for rapid clinical intervention and management. Cardiovascular devices including the CardioMicroelectromechanical (CardioMEMS) device, implantable loop recorder, and right ventricular (RV) leadless pacemaker are now widely used for treatment and monitoring of advanced cardiac conditions, as many of these devices have been shown to significantly improve patient outcomes. Additionally, hemodynamic monitoring devices have shown utility in monitoring patients with aortic aneurysms after endovascular aortic repair (EVAR) for early detection of Type I and Type II endoleaks. There is limited published data regarding the imaging features of these devices. As these devices become more widely used, it is important for radiologists to become familiar with the normal imaging features and potential complications. The goal of this review is to summarize the data regarding the use of leadless cardiovascular devices including the CardioMEMS device, implantable loop recorder, and RV leadless pacemaker, and to present cases demonstrating their utility and normal imaging features.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declared no conflicts of interest.
Figures




References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

