Differential effects of angiotensin II type I receptor blockers on reducing intraocular pressure and TGFβ signaling in the mouse retina
- PMID: 30092004
- PMCID: PMC6084929
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0201719
Differential effects of angiotensin II type I receptor blockers on reducing intraocular pressure and TGFβ signaling in the mouse retina
Abstract
Purpose: Angiotensin II type 1 receptor blockers (ARBs) have been investigated for their neuroprotective and intraocular pressure (IOP) lowering effects in treating glaucoma, but the reports have been inconsistent possibly because different compounds and models have been used. Here we selected three ARBs for head-to-head comparisons of their effects on IOP and transforming growth factor β (TGFβ) signaling, which is believed to play an important role in glaucoma pathogenesis.
Methods: Three ARBs (losartan, irbesartan or telmisartan) or vehicle controls were administered via chow to C57BL/6J mice for up to 7 days. Drug concentrations in the eye, brain, and plasma were evaluated by liquid chromatography mass spectrometry. Cohorts of mice were randomly assigned to different treatments. IOP and blood pressure were measured before and after ARB treatment. Effects of ARBs on TGFβ signaling in the retina were evaluated by phosphorylated Smad2 (pSmad2) immunohistochemistry.
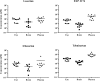
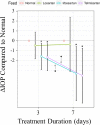
Results: Physiologically relevant concentrations of losartan, irbesartan and telmisartan were detected in eye, brain and plasma after drug administration (n = 11 mice/treatment). Blood pressure was significantly reduced by all ARBs compared to vehicle-fed controls (all p-values < 0.001, n = 8-15 mice/treatment). Compared to vehicle control, IOP was significantly reduced by irbesartan (p = 0.030) and telmisartan (p = 0.019), but not by losartan (n = 14-17 mice/treatment). Constitutive pSmad2 fluorescence observed in retinal ganglion cells was significantly reduced by telmisartan (p = 0.034), but not by losartan or irbesartan (n = 3-4 mice/treatment).
Conclusions: Administration via chow is an effective delivery method for ARBs, as evidenced by lowered blood pressure. ARBs vary in their abilities to lower IOP or reduce TGFβ signaling. Considering the significant roles of IOP and TGFβ in glaucoma pathogenesis, specific ARBs with dual effects, such as telmisartan, may be more effective than other ARBs for treating glaucoma.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Dimorphic effects of transforming growth factor-β signaling during aortic aneurysm progression in mice suggest a combinatorial therapy for Marfan syndrome.Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2015 Apr;35(4):911-7. doi: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.114.305150. Epub 2015 Jan 22. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2015. PMID: 25614286 Free PMC article.
-
The effects of different angiotensin II type 1 receptor blockers on the regulation of the ACE-AngII-AT1 and ACE2-Ang(1-7)-Mas axes in pressure overload-induced cardiac remodeling in male mice.J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2016 Aug;97:180-90. doi: 10.1016/j.yjmcc.2016.05.012. Epub 2016 May 19. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2016. PMID: 27210827
-
Angiotensin Receptor Blockers in cyclodextrin nanoparticle eye drops: Ocular pharmacokinetics and pharmacologic effect on intraocular pressure.Acta Ophthalmol. 2021 Jun;99(4):376-382. doi: 10.1111/aos.14639. Epub 2020 Nov 16. Acta Ophthalmol. 2021. PMID: 33191620
-
Effects of telmisartan, irbesartan, valsartan, candesartan, and losartan on cancers in 15 trials enrolling 138,769 individuals.J Hypertens. 2011 Apr;29(4):623-35. doi: 10.1097/HJH.0b013e328344a7de. J Hypertens. 2011. PMID: 21358417 Review.
-
Telmisartan: a different angiotensin II receptor blocker protecting a different population?J Int Med Res. 2009 Nov-Dec;37(6):1662-79. doi: 10.1177/147323000903700602. J Int Med Res. 2009. PMID: 20146864 Review.
Cited by
-
Losartan controls immune checkpoint blocker-induced edema and improves survival in glioblastoma mouse models.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2023 Feb 7;120(6):e2219199120. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2219199120. Epub 2023 Feb 1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2023. PMID: 36724255 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization of TGF-β by Induced Oxidative Stress in Human Trabecular Meshwork Cells.Antioxidants (Basel). 2021 Jan 13;10(1):107. doi: 10.3390/antiox10010107. Antioxidants (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33451157 Free PMC article.
-
Angiotensin II Induces Oxidative Stress and Endothelial Dysfunction in Mouse Ophthalmic Arteries via Involvement of AT1 Receptors and NOX2.Antioxidants (Basel). 2021 Aug 2;10(8):1238. doi: 10.3390/antiox10081238. Antioxidants (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34439486 Free PMC article.
-
The use of angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors vs. angiotensin receptor blockers and cognitive decline in Alzheimer's disease: the importance of blood-brain barrier penetration and APOE ε4 carrier status.Alzheimers Res Ther. 2021 Feb 11;13(1):43. doi: 10.1186/s13195-021-00778-8. Alzheimers Res Ther. 2021. PMID: 33573702 Free PMC article.
-
Optic neuropathy associated with TGFβ dysregulation in mice with a glaucoma-causative mutation of ADAMTS10.Matrix Biol. 2022 Nov;113:83-99. doi: 10.1016/j.matbio.2022.10.001. Epub 2022 Oct 8. Matrix Biol. 2022. PMID: 36216203 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Karnik SS, Unal H, Kemp JR, Tirupula KC, Eguchi S, Vanderheyden PM, et al. International Union of Basic and Clinical Pharmacology. XCIX. Angiotensin Receptors: Interpreters of Pathophysiological Angiotensinergic Stimuli [corrected]. Pharmacol Rev. 2015;67(4):754–819. 10.1124/pr.114.010454 ; PubMed Central PMCID: PMCPMC4630565. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

