Generalized logistic functions in modelling emergence of Brassica napus L
- PMID: 30092006
- PMCID: PMC6085063
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0201980
Generalized logistic functions in modelling emergence of Brassica napus L
Abstract
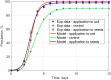
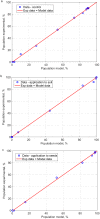
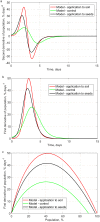
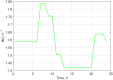
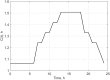
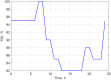
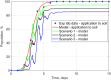
The objective of this study was to determine whether generalized logistic functions (Richards model with time shift) may be used to predict emergence of winter rapeseed (Brassica napus L.) after its seed treatment with plant extracts from Taraxacum officinale roots under controlled environment conditions. Emergence analyses were conducted for winter rape whose seeds were treated with a plant extract and for the non-treated seeds sown to the soil at the site of earlier point application of the extract. Curves were plotted for experimental data by minimizing the square sum of differences between the experimental data and the mathematical model. To evaluate model fit, the mean squared error was divided into four factors. Computing modelling efficiency coefficients were also introduced to enable complete analysis. Results of simulation research demonstrate that the determined parameters of curves (e.g. values of growth parameters, time shift or the upper limit of population) describing the number of seedlings in the function of time stayed compliant to the interpretation with regard to the biology of the analyzed processes. The proposed mathematical description based on generalized logistic functions showed extraordinary fit (r = 0.999) to the experimental data, which makes it highly useful in predictive control of rapeseed emergence. In addition, the study enabled concluding that plant extracts application to the soil allowed achieving a higher maximal emergence rate compared to the control sample. The application of the plant extracts increased the final population of rapeseed and significantly accelerated the occurrence of the maximal emergence rate.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Effects of seed priming treatments on the germination and development of two rapeseed (Brassica napus L.) varieties under the co-influence of low temperature and drought.PLoS One. 2021 Sep 16;16(9):e0257236. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0257236. eCollection 2021. PLoS One. 2021. PMID: 34529689 Free PMC article.
-
A novel Brassica-rhizotron system to unravel the dynamic changes in root system architecture of oilseed rape under phosphorus deficiency.Ann Bot. 2016 Aug;118(2):173-84. doi: 10.1093/aob/mcw083. Epub 2016 Jun 8. Ann Bot. 2016. PMID: 27279575 Free PMC article.
-
Ultrasonic seed treatment improved cadmium (Cd) tolerance in Brassica napus L.Ecotoxicol Environ Saf. 2019 Dec 15;185:109659. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoenv.2019.109659. Epub 2019 Sep 18. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf. 2019. PMID: 31541946
-
The high-affinity transporter BnPHT1;4 is involved in phosphorus acquisition and mobilization for facilitating seed germination and early seedling growth of Brassica napus.BMC Plant Biol. 2019 Apr 25;19(1):156. doi: 10.1186/s12870-019-1765-3. BMC Plant Biol. 2019. PMID: 31023216 Free PMC article.
-
Rapeseed species and environmental concerns related to loss of seeds of genetically modified oilseed rape in Japan.GM Crops. 2010 May-Jun;1(3):143-56. doi: 10.4161/gmcr.1.3.12761. GM Crops. 2010. PMID: 21844669 Review.
Cited by
-
Plant Material as a Novel Tool in Designing and Formulating Modern Biostimulants-Analysis of Botanical Extract from Linum usitatissimum L.Materials (Basel). 2021 Nov 4;14(21):6661. doi: 10.3390/ma14216661. Materials (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34772188 Free PMC article.
-
Extended Hopanoid Loss Reduces Bacterial Motility and Surface Attachment and Leads to Heterogeneity in Root Nodule Growth Kinetics in a Bradyrhizobium-Aeschynomene Symbiosis.Mol Plant Microbe Interact. 2019 Oct;32(10):1415-1428. doi: 10.1094/MPMI-04-19-0111-R. Epub 2019 Aug 27. Mol Plant Microbe Interact. 2019. PMID: 31170026 Free PMC article.
-
The impact of government measures and human mobility trend on COVID-19 related deaths in the UK.Transp Res Interdiscip Perspect. 2020 Jul;6:100167. doi: 10.1016/j.trip.2020.100167. Epub 2020 Jul 4. Transp Res Interdiscip Perspect. 2020. PMID: 34173458 Free PMC article.
-
Bayesian calibration, process modeling and uncertainty quantification in biotechnology.PLoS Comput Biol. 2022 Mar 7;18(3):e1009223. doi: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1009223. eCollection 2022 Mar. PLoS Comput Biol. 2022. PMID: 35255090 Free PMC article.
-
Growth modeling approach with the Verhulst coexistence dynamic properties for regulation purposes.Theory Biosci. 2023 Sep;142(3):221-234. doi: 10.1007/s12064-023-00397-x. Epub 2023 Jul 8. Theory Biosci. 2023. PMID: 37421497 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Czerwińska E, Szparaga A. The vitality and healthiness of oil seeds treated by plant extracts. Acta Sci. Pol. Technica Agraria. 2015; 14(1,2): 47–59 (in Polish with English abstract).
-
- Czerwińska E, Szparaga A.Antibacterial and antifungal activity of plant extracts. Rocznik Ochrona Srodowiska. 2015; 17(1): 209–229.
-
- Czerwińska E, Szparaga A, Piskier T, Deszcz E. Effect of the application methods of natural plant extract on emergence of beets. Journal of Research and Applications in Agricultural Engineering. 2016; 61(3): 67–71.
-
- Adaszyńska M, Swarcewicz M, Markowska-Szczupak A. Comparison of chemical composition and antimicrobial activity of lavender varieties from Poland. Progress of Phytotherapy. 2013; 2: 90–96 (in Polish with English abstract). - PubMed
-
- Bošković M, Baltić ŽM, Ivanović J, Đurić J, Lončina J, Dokmanović M, et al. Use of essential oils in order to prevent foodborneillnesses caused by pathogens in meat. Tehnologija mesa. 2015; 54(1): 14–20.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

