Control of transmembrane charge transfer in cytochrome c oxidase by the membrane potential
- PMID: 30093670
- PMCID: PMC6085328
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-018-05615-5
Control of transmembrane charge transfer in cytochrome c oxidase by the membrane potential
Abstract
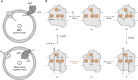
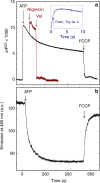
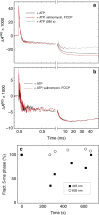
The respiratory chain in mitochondria is composed of membrane-bound proteins that couple electron transfer to proton translocation across the inner membrane. These charge-transfer reactions are regulated by the proton electrochemical gradient that is generated and maintained by the transmembrane charge transfer. Here, we investigate this feedback mechanism in cytochrome c oxidase in intact inner mitochondrial membranes upon generation of an electrochemical potential by hydrolysis of ATP. The data indicate that a reaction step that involves proton uptake to the catalytic site and presumably proton translocation is impaired by the potential, but electron transfer is not affected. These results define the order of electron and proton-transfer reactions and suggest that the proton pump is regulated by the transmembrane electrochemical gradient through control of internal proton transfer rather than by control of electron transfer.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Proton-coupled electron transfer drives the proton pump of cytochrome c oxidase.Nature. 2006 Apr 6;440(7085):829-32. doi: 10.1038/nature04619. Nature. 2006. PMID: 16598262
-
Structural Changes and Proton Transfer in Cytochrome c Oxidase.Sci Rep. 2015 Aug 27;5:12047. doi: 10.1038/srep12047. Sci Rep. 2015. PMID: 26310633 Free PMC article.
-
Internal charge transfer in cytochrome c oxidase at a limited proton supply: proton pumping ceases at high pH.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2009 Jun;1790(6):552-7. doi: 10.1016/j.bbagen.2009.03.023. Epub 2009 Mar 31. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2009. PMID: 19344748
-
Revealing various coupling of electron transfer and proton pumping in mitochondrial respiratory chain.Curr Opin Struct Biol. 2013 Aug;23(4):526-38. doi: 10.1016/j.sbi.2013.06.013. Epub 2013 Jul 16. Curr Opin Struct Biol. 2013. PMID: 23867107 Review.
-
Coupled proton and electron transfer reactions in cytochrome oxidase.Front Biosci. 2004 Jan 1;9:581-91. doi: 10.2741/1237. Front Biosci. 2004. PMID: 14766393 Review.
Cited by
-
Mitochondrial metabolism and cancer therapeutic innovation.Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2025 Aug 4;10(1):245. doi: 10.1038/s41392-025-02311-x. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2025. PMID: 40754534 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Key Role of COA6 in Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma: Metabolic Reprogramming and Regulation of the Immune Microenvironment.J Cell Mol Med. 2025 Jul;29(13):e70685. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.70685. J Cell Mol Med. 2025. PMID: 40596639 Free PMC article.
-
Recent progress in experimental studies on the catalytic mechanism of cytochrome c oxidase.Front Chem. 2023 May 4;11:1108190. doi: 10.3389/fchem.2023.1108190. eCollection 2023. Front Chem. 2023. PMID: 37214485 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The flexible chain: regulation of structure and activity of ETC complexes defines rate of ATP synthesis and sites of superoxide generation.Biophys Rev. 2025 Jan 25;17(1):55-88. doi: 10.1007/s12551-025-01270-5. eCollection 2025 Feb. Biophys Rev. 2025. PMID: 40060020 Review.
-
Broadband fluorescence reveals mechanistic differences in excited-state proton transfer to protic and aprotic solvents.Chem Sci. 2020 Jul 8;11(30):7963-7971. doi: 10.1039/d0sc03316b. Chem Sci. 2020. PMID: 34094165 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

