Robotic Kidney Transplantation from a Brain-Dead Deceased Donor in a Patient with Autosomal Dominant Polycystic Kidney Disease: First Case Report
- PMID: 30094337
- PMCID: PMC6083208
- DOI: 10.1089/cren.2018.0050
Robotic Kidney Transplantation from a Brain-Dead Deceased Donor in a Patient with Autosomal Dominant Polycystic Kidney Disease: First Case Report
Abstract
Background: Autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease (ADPKD) is a common cause of end-stage renal disease (ESRD) and may pose significant technical challenges for kidney transplantation. Recently, robot-assisted kidney transplantation (RAKT) has been shown to achieve excellent patient and graft outcomes while reducing surgical morbidity. However, the vast majority of RAKT performed so far were from living donors and no studies reported the outcomes of RAKT in patients with ADPKD. Case Presentation: Herein, we describe the first successful case of RAKT from a brain-dead deceased donor in a 37-year-old patient with ESRD due to ADPKD. Conclusion: Our case highlights that RAKT can be safely performed by experienced robotic surgeons even in selected complex recipients such as patients with ADPKD and using grafts from deceased donors.
Keywords: autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease; brain-dead deceased donor; case report; kidney transplantation; robotics.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures
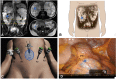


References
-
- Jean RA, Alexandre M, Yoo PS. Kidney transplantation with and without native nephrectomy for polycystic kidney disease: Results of the national inpatient sample and the rationale for a 2-staged procedure. J Am Coll Surg 2018;226:1079–1084 - PubMed
-
- Menon M, Sood A, Bhandari M, et al. . Robotic kidney transplantation with regional hypothermia: A step-by-step description of the Vattikuti Urology Institute–Medanta Technique (IDEAL Phase 2a). Eur Urol 2014;65:991–1000 - PubMed
-
- Marconi L, Figueiredo A. Chapter 14: Cadaver donor organ procurement: Technical aspects and surgical options. In: Figueiredo A, Lledò-Garcìa E, eds. European Texbook on Kidney Tranplantation (ESTU-EAU), 1st ed. 2017. SBN/EAN 9789492671004. © EAU Section Office
-
- Sood A, Ghani KR, Ahlawat R, et al. . Application of the statistical process control method for prospective patient safety monitoring during the learning phase: Robotic kidney transplantation with regional hypothermia (IDEAL phase 2a-b). Eur Urol 2014;66:371–378 - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
