Current Level of Glycemic Control and Clinical Inertia in Subjects Using Insulin for the Treatment of Type 1 and Type 2 Diabetes in the Czech Republic and the Slovak Republic: Results of a Multinational, Multicenter, Observational Survey (DIAINFORM)
- PMID: 30094784
- PMCID: PMC6167301
- DOI: 10.1007/s13300-018-0485-2
Current Level of Glycemic Control and Clinical Inertia in Subjects Using Insulin for the Treatment of Type 1 and Type 2 Diabetes in the Czech Republic and the Slovak Republic: Results of a Multinational, Multicenter, Observational Survey (DIAINFORM)
Abstract
Introduction: The aim of the study was to determine the level of metabolic control in type 1 diabetes mellitus (T1DM) and type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) patients in the Czech and Slovak Republics.
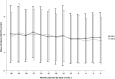
Methods: A non-interventional prospective (observational) study was conducted from January 2015 until April 2016 in routine clinical practice settings at 141 centers in the Czech and Slovak Republics. Data were analyzed from a total of 425 patients with T1DM and 1034 patients with T2DM, proportionally corresponding to the number of patients in both countries. The primary objective of the study was to determine the percentage of patients with HbA1c < 7% (53 mmol/mol).
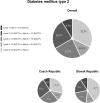
Results: Patients with T1DM: In this group of patients (55.8% males, mean age 45.9 ± 14.83 years, BMI 25.8 ± 4.21 kg/m², diabetes duration 12.1 ± 9.44 years), 29.9% reached HbA1c levels < 53 mmol/mol. Patients with T2DM: In this group of patients (50.3% male, mean age 63.9 ± 9.65 years, BMI 31.0 ± 5.19 kg/m², diabetes duration 12.4 ± 7.47 years, duration of insulin therapy 5.8 ± 4.71 years), 33.4% reached HbA1c levels < 53 mmol/mol.
Conclusion: The overall percentage of patients with HbA1c < 53 mmol/mol in the T1DM group was 29.9% and in the T2DM group was 33.4%. Despite an increasing number of treatment options, most patients still fail to reach the recommended HbA1c targets.
Funding: Sanofi, Czech Republic.
Keywords: Clinical inertia; HbA1c; Insulin therapy; Metabolic control; Type 1 diabetes; Type 2 diabetes.
Figures

References
-
- Stratton IM, Adler AI, Neil HA, Matthews DR, Manley SE, Cull CA, et al. Association of glycaemia with macrovascular and microvascular complications of type 2 diabetes UK prospective diabetes study (UKPDS 35): prospective observational study. Br Med J. 2000;321:405–412. doi: 10.1136/bmj.321.7258.405. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

