Emerging Roles for Intermolecular RNA-RNA Interactions in RNP Assemblies
- PMID: 30096311
- PMCID: PMC6200146
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2018.07.023
Emerging Roles for Intermolecular RNA-RNA Interactions in RNP Assemblies
Abstract
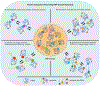
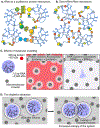
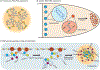
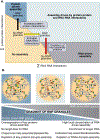
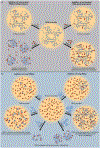
Eukaryotic cells contain large assemblies of RNA and protein, referred to as ribonucleoprotein (RNP) granules, which include cytoplasmic P-bodies, stress granules, and neuronal and germinal granules, as well as nuclear paraspeckles, Cajal bodies, and RNA foci formed from repeat expansion RNAs. Recent evidence argues that intermolecular RNA-RNA interactions play a role in forming and determining the composition of certain RNP granules. We hypothesize that intermolecular RNA-RNA interactions are favored in cells yet are limited by RNA-binding proteins, helicases, and ribosomes, thereby allowing normal RNA function. An over-abundance of intermolecular RNA-RNA interactions may be toxic since perturbations that increase RNA-RNA interactions such as long repeat expansion RNAs, arginine-containing dipeptide repeat polypeptides, and sequestration or loss of abundant RNA-binding proteins can contribute to degenerative diseases.
Copyright © 2018 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures

References
-
- Aumiller WM Jr., Pir Cakmak F, Davis BW, and Keating CD (2016). RNA-Based Coacervates as a Model for Membraneless Organelles: Formation, Properties, and Interfacial Liposome Assembly. Langmuir acs.langmuir.6b02499. - PubMed
-
- Aw JGA, Shen Y, Wilm A, Sun M, Lim XN, Boon K-L, Tapsin S, Chan Y-S, Tan C-P, Sim AYL, et al. (2016). In Vivo Mapping of Eukaryotic RNA Interactomes Reveals Principles of Higher-Order Organization and Regulation. Molecular Cell 62, 603–617. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

