Evaluation of 18F-RO-948 PET for Quantitative Assessment of Tau Accumulation in the Human Brain
- PMID: 30097505
- PMCID: PMC6278898
- DOI: 10.2967/jnumed.118.214437
Evaluation of 18F-RO-948 PET for Quantitative Assessment of Tau Accumulation in the Human Brain
Abstract
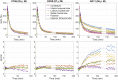
The availability of tau PET radioligands enables quantitative assessment of tau density and distribution in the human brain. We evaluated the kinetics of a novel radioligand, 18F-RO-948 (previously referred to as 18F-RO6958948), and its ability to identify tau positivity in individual patients with mild Alzheimer disease (AD). Methods: Eleven subjects with amyloid-positive mild AD, 5 amyloid-negative older control subjects (OC), and 5 younger control subjects (YC) completed 1 or 2 (4 AD and 5 OC) PET scans with 18F-RO-948 for 90, 120, or 200 min. The kinetics of the radioligand was evaluated with standard compartmental and noncompartmental models (with plasma data in 70% of cases), tissue-reference methods, and SUV ratio. These approaches were applied to assess the ability of 18F-RO-948 to discriminate AD subjects from OC subjects. Results: The plasma reference graphical analysis appeared to be the optimal method of quantification for 18F-RO-948, yielding strictly time-consistent values of distribution volume and distribution volume ratio at 90 min against the analyses at 120 and 200 min. The reference tissue graphical analysis and SUV ratio were cross-validated against plasma reference graphical analysis. Test-retest evaluation showed excellent reproducibility. A proposed novel index of tau load, the regional tau-positive fraction, showed high values in the medial and lateral temporal and parietal regions in AD and successfully separated AD subjects from OC and YC subjects with a significant margin. Conclusion:18F-RO-948 appears to be a promising radioligand for quantitative imaging of tau in the brain of AD patients.
Keywords: 18F-RO6958948 for tau imaging; Alzheimer disease; PET; neurology; radiotracer tissue kinetics.
© 2018 by the Society of Nuclear Medicine and Molecular Imaging.
Figures






References
-
- Villemagne VL, Fodero-Tavoletti MT, Masters CL, Rowe CC. Tau imaging: early progress and future directions. Lancet Neurol. 2015;14:114–124. - PubMed
-
- Iqbal K, Liu F, Gong CX. Tau and neurodegenerative disease: the story so far. Nat Rev Neurol. 2016;12:15–27. - PubMed
-
- Braak H, Braak E. Diagnostic criteria for neuropathologic assessment of Alzheimer’s disease. Neurobiol Aging. 1997;18(suppl):S85–S88. - PubMed
-
- Delacourte A, David JP, Sergeant N, et al. The biochemical pathway of neurofibrillary degeneration in aging and Alzheimer’s disease. Neurology. 1999;52:1158–1165. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
