Targeting AURKA-CDC25C axis to induce synthetic lethality in ARID1A-deficient colorectal cancer cells
- PMID: 30097580
- PMCID: PMC6086874
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-018-05694-4
Targeting AURKA-CDC25C axis to induce synthetic lethality in ARID1A-deficient colorectal cancer cells
Abstract
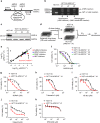
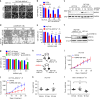
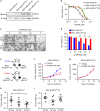
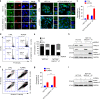
ARID1A, a component of the SWI/SNF chromatin remodeling complex, is a tumor suppressor with a high frequency of inactivating mutations in many cancers. Therefore, ARID1A deficiency has been exploited therapeutically for treating cancer. Here we show that ARID1A has a synthetic lethal interaction with aurora kinase A (AURKA) in colorectal cancer (CRC) cells. Pharmacological and genetic perturbations of AURKA selectively inhibit the growth of ARID1A-deficient CRC cells. Mechanistically, ARID1A occupies the AURKA gene promoter and negatively regulates its transcription. Cells lacking ARID1A show enhanced AURKA transcription, which leads to the persistent activation of CDC25C, a key protein for G2/M transition and mitotic entry. Inhibiting AURKA activity in ARID1A-deficient cells significantly increases G2/M arrest and induces cellular multinucleation and apoptosis. This study shows a novel synthetic lethality interaction between ARID1A and AURKA and indicates that pharmacologically inhibiting the AURKA-CDC25C axis represents a novel strategy for treating CRC with ARID1A loss-of-function mutations.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Wang W. The SWI/SNF family of ATP-dependent chromatin remodelers: similar mechanisms for diverse functions. Curr. Top. Microbiol. Immunol. 2003;274:143–169. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

