Regularization strategies in statistical image reconstruction of low-dose x-ray CT: A review
- PMID: 30098050
- PMCID: PMC6181784
- DOI: 10.1002/mp.13123
Regularization strategies in statistical image reconstruction of low-dose x-ray CT: A review
Abstract
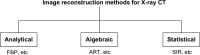
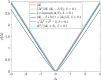
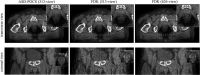
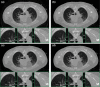
Statistical image reconstruction (SIR) methods have shown potential to substantially improve the image quality of low-dose x-ray computed tomography (CT) as compared to the conventional filtered back-projection (FBP) method. According to the maximum a posteriori (MAP) estimation, the SIR methods are typically formulated by an objective function consisting of two terms: (a) a data-fidelity term that models imaging geometry and physical detection processes in projection data acquisition, and (b) a regularization term that reflects prior knowledge or expectations of the characteristics of the to-be-reconstructed image. SIR desires accurate system modeling of data acquisition, while the regularization term also has a strong influence on the quality of reconstructed images. A variety of regularization strategies have been proposed for SIR in the past decades, based on different assumptions, models, and prior knowledge. In this paper, we review the conceptual and mathematical bases of these regularization strategies and briefly illustrate their efficacies in SIR of low-dose CT.
Keywords: low dose; regularization; statistical image reconstruction; x-ray CT.
© 2018 American Association of Physicists in Medicine.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no relevant conflict of interest to disclose.
Figures








References
-
- Brenner DJ, Hall EJ. Computed tomography – an increasing source of radiation exposure. N Engl J Med. 2007;357:2277–2284. - PubMed
-
- Einstein AJ, Henzlova MJ, Rajagopalan S. Estimating risk of cancer associated with radiation exposure from 64‐slice computed tomography coronary angiography. JAMA. 2007;298:317–323. - PubMed
-
- Kalender WA, Wolf H, Suess C. Dose reduction in CT by anatomically adapted tube current modulation. II. Phantom measurements. Med Phys. 1999;26:2248–2253. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

