Combined inhibition of MEK and PI3K pathways overcomes acquired resistance to EGFR-TKIs in non-small cell lung cancer
- PMID: 30098066
- PMCID: PMC6172047
- DOI: 10.1111/cas.13763
Combined inhibition of MEK and PI3K pathways overcomes acquired resistance to EGFR-TKIs in non-small cell lung cancer
Abstract
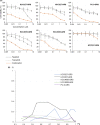
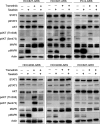
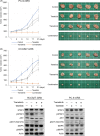
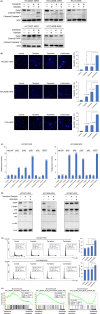
Compensatory activation of the signal transduction pathways is one of the major obstacles for the targeted therapy of non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). Herein, we present the therapeutic strategy of combined targeted therapy against the MEK and phosphoinositide-3 kinase (PI3K) pathways for acquired resistance to epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs) in NSCLC. We investigated the efficacy of combined trametinib plus taselisib therapy using experimentally established EGFR-TKI-resistant NSCLC cell lines. The results showed that the feedback loop between MEK/ERK and PI3K/AKT pathways had developed in several resistant cell lines, which caused the resistance to single-agent treatment with either inhibitor alone. Meanwhile, the combined therapy successfully regulated the compensatory activation of the key intracellular signals and synergistically inhibited the cell growth of those cells in vitro and in vivo. The resistance mechanisms for which the dual kinase inhibitor therapy proved effective included (MET) mesenchymal-epithelial transition factor amplification, induction of epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition (EMT) and EGFR T790M mutation. In further analysis, the combination therapy induced the phosphorylation of p38 MAPK signaling, leading to the activation of apoptosis cascade. Additionally, long-term treatment with the combination therapy induced the conversion from EMT to mesenchymal-to-epithelial transition in the resistant cell line harboring EMT features, restoring the sensitivity to EGFR-TKI. In conclusion, our results indicate that the combined therapy using MEK and PI3K inhibitors is a potent therapeutic strategy for NSCLC with the acquired resistance to EGFR-TKIs.
Keywords: MEK inhibitor; PI3K inhibitor; acquired resistance; compensatory activation; non-small cell lung cancer.
© 2018 The Authors. Cancer Science published by John Wiley & Sons Australia, Ltd on behalf of Japanese Cancer Association.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Polyphyllin I Overcomes EMT-Associated Resistance to Erlotinib in Lung Cancer Cells via IL-6/STAT3 Pathway Inhibition.Biol Pharm Bull. 2017 Aug 1;40(8):1306-1313. doi: 10.1248/bpb.b17-00271. Epub 2017 May 18. Biol Pharm Bull. 2017. PMID: 28515374
-
The HSP90 inhibitor, NVP-AUY922, sensitizes KRAS-mutant non-small cell lung cancer with intrinsic resistance to MEK inhibitor, trametinib.Cancer Lett. 2016 Mar 1;372(1):75-81. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2015.12.015. Epub 2015 Dec 23. Cancer Lett. 2016. PMID: 26723875
-
Polo-like kinase 1 inhibition diminishes acquired resistance to epidermal growth factor receptor inhibition in non-small cell lung cancer with T790M mutations.Oncotarget. 2016 Jul 26;7(30):47998-48010. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.10332. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 27384992 Free PMC article.
-
Features and efficacy of triple-targeted therapy for patients with EGFR-mutant non-small-cell lung cancer with acquired BRAF alterations who are resistant to epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitors.ESMO Open. 2024 Oct;9(10):103935. doi: 10.1016/j.esmoop.2024.103935. Epub 2024 Oct 9. ESMO Open. 2024. PMID: 39389004 Free PMC article.
-
Current mechanism of acquired resistance to epidermal growth factor receptor-tyrosine kinase inhibitors and updated therapy strategies in human nonsmall cell lung cancer.J Cancer Res Ther. 2016 Dec;12(Supplement):C131-C137. doi: 10.4103/0973-1482.200613. J Cancer Res Ther. 2016. PMID: 28230005 Review.
Cited by
-
Treatment of advanced non-small cell lung cancer with driver mutations: current applications and future directions.Front Med. 2023 Feb;17(1):18-42. doi: 10.1007/s11684-022-0976-4. Epub 2023 Feb 23. Front Med. 2023. PMID: 36848029 Review.
-
Yang-Yin-Jie-Du decoction overcomes gefitinib resistance in non-small cell lung cancer via down-regulation of the PI3K/Akt signalling pathway.Pharm Biol. 2021 Dec;59(1):1294-1304. doi: 10.1080/13880209.2021.1972122. Pharm Biol. 2021. PMID: 34543169 Free PMC article.
-
Longitudinal Monitoring of EGFR and PIK3CA Mutations by Saliva-Based EFIRM in Advanced NSCLC Patients With Local Ablative Therapy and Osimertinib Treatment: Two Case Reports.Front Oncol. 2020 Jul 24;10:1240. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2020.01240. eCollection 2020. Front Oncol. 2020. PMID: 32793495 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanisms of resistance to targeted therapy and immunotherapy in non-small cell lung cancer: promising strategies to overcoming challenges.Front Immunol. 2024 Apr 9;15:1366260. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1366260. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 38655260 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cooperation between Prostaglandin E2 and Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor in Cancer Progression: A Dual Target for Cancer Therapy.Cancers (Basel). 2023 Apr 19;15(8):2374. doi: 10.3390/cancers15082374. Cancers (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37190301 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Lynch TJ, Bell DW, Sordella R, et al. Activating mutations in the epidermal growth factor receptor underlying responsiveness of non‐small‐cell lung cancer to gefitinib. N Engl J Med. 2004;350:2129‐2139. - PubMed
-
- Paez JG, Janne PA, Lee JC, et al. EGFR mutations in lung cancer: correlation with clinical response to gefitinib therapy. Science. 2004;304:1497‐1500. - PubMed
-
- Kobayashi S, Boggon TJ, Dayaram T, et al. EGFR mutation and resistance of non‐small‐cell lung cancer to gefitinib. N Engl J Med. 2005;352:786‐792. - PubMed
-
- Engelman JA, Zejnullahu K, Mitsudomi T, et al. MET amplification leads to gefitinib resistance in lung cancer by activating ERBB3 signaling. Science. 2007;316:1039‐1043. - PubMed
-
- Yano S, Wang W, Li Q, et al. Hepatocyte growth factor induces gefitinib resistance of lung adenocarcinoma with epidermal growth factor receptor‐activating mutations. Cancer Res. 2008;68:9479‐9487. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

