A One-Penny Imputed Genome from Next-Generation Reference Panels
- PMID: 30100085
- PMCID: PMC6128308
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ajhg.2018.07.015
A One-Penny Imputed Genome from Next-Generation Reference Panels
Abstract
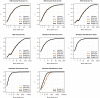
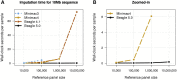
Genotype imputation is commonly performed in genome-wide association studies because it greatly increases the number of markers that can be tested for association with a trait. In general, one should perform genotype imputation using the largest reference panel that is available because the number of accurately imputed variants increases with reference panel size. However, one impediment to using larger reference panels is the increased computational cost of imputation. We present a new genotype imputation method, Beagle 5.0, which greatly reduces the computational cost of imputation from large reference panels. We compare Beagle 5.0 with Beagle 4.1, Impute4, Minimac3, and Minimac4 using 1000 Genomes Project data, Haplotype Reference Consortium data, and simulated data for 10k, 100k, 1M, and 10M reference samples. All methods produce nearly identical accuracy, but Beagle 5.0 has the lowest computation time and the best scaling of computation time with increasing reference panel size. For 10k, 100k, 1M, and 10M reference samples and 1,000 phased target samples, Beagle 5.0's computation time is 3× (10k), 12× (100k), 43× (1M), and 533× (10M) faster than the fastest alternative method. Cost data from the Amazon Elastic Compute Cloud show that Beagle 5.0 can perform genome-wide imputation from 10M reference samples into 1,000 phased target samples at a cost of less than one US cent per sample.
Keywords: GWAS; genome-wide association study; genotype imputation.
Copyright © 2018 American Society of Human Genetics. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures



References
-
- Marchini J., Howie B. Genotype imputation for genome-wide association studies. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2010;11:499–511. - PubMed
-
- Marchini J., Howie B., Myers S., McVean G., Donnelly P. A new multipoint method for genome-wide association studies by imputation of genotypes. Nat. Genet. 2007;39:906–913. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

