Classifications of Mastoid and Middle Ear Surgery: A Scoping Review
- PMID: 30100541
- PMCID: PMC6354474
- DOI: 10.5152/iao.2018.5570
Classifications of Mastoid and Middle Ear Surgery: A Scoping Review
Abstract
Objectives: The aim of this scoping review was to evaluate existing classifications of surgical procedures of the middle ear and mastoid and find a suitable classification that could serve as an international standard.
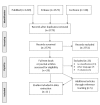
Materials and methods: Scoping review with a systematic literature search using reference tracking and a syntax including all surgical procedures in mastoid and middle ear surgery and their synonyms. Studies were selected based on inclusion and exclusion criteria.
Results: Eleven reported classifications were included; six of which focused on middle ear surgery, two on mastoid surgery, and three on both. However, none of the classifications included all current surgical procedures of mastoid and middle ear surgery.
Conclusion: Many classifications have been proposed for innumerable surgical techniques in middle ear and mastoid surgery. Some are outdated, some are incomplete, most are not widely accepted, and only few correspond with all current surgical techniques.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Arksey H, O’Malley L. Scoping studies: towards a methodological framework. Int J Soc Res Methodol. 2005;8:19–32. doi: 10.1080/1364557032000119616. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources