An end to end workflow for differential gene expression using Affymetrix microarrays
- PMID: 30101006
- PMCID: PMC6063319
- DOI: 10.12688/f1000research.8967.2
An end to end workflow for differential gene expression using Affymetrix microarrays
Abstract
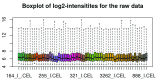
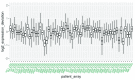
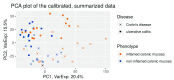
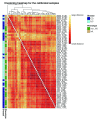
In this article, we walk through an end-to-end Affymetrix microarray differential expression workflow using Bioconductor packages. This workflow is directly applicable to current "Gene'' type arrays, e.g.the HuGene or MoGene arrays, but can easily be adapted to similar platforms. The data analyzed here is a typical clinical microarray data set that compares inflamed and non-inflamed colon tissue in two disease subtypes. For each disease, the differential gene expression between inflamed- and non-inflamed colon tissue was analyzed. We will start from the raw data CEL files, show how to import them into a Bioconductor ExpressionSet, perform quality control and normalization and finally differential gene expression (DE) analysis, followed by some enrichment analysis.
Keywords: gene expression; microarray.
Conflict of interest statement
No competing interests were disclosed.
Figures



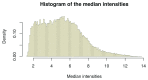
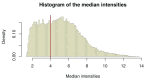

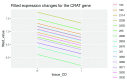
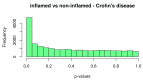





References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

