Early feeding practices in infants with phenylketonuria across Europe
- PMID: 30101073
- PMCID: PMC6082991
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ymgmr.2018.07.008
Early feeding practices in infants with phenylketonuria across Europe
Abstract
Background: In infants with phenylketonuria (PKU), dietary management is based on lowering and titrating phenylalanine (Phe) intake from breast milk or standard infant formula in combination with a Phe-free infant formula in order to maintain blood Phe levels within target range. Professionals use different methods to feed infants with PKU and our survey aimed to document practices across Europe.
Methods: We sent a cross sectional, survey monkey® questionnaire to European health professionals working in IMD. It contained 31 open and multiple-choice questions. The results were analysed according to different geographical regions.
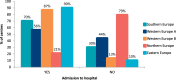
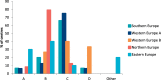
Results: Ninety-five centres from 21 countries responded. Over 60% of centres commenced diet in infants by age 10 days, with 58% of centres implementing newborn screening by day 3 post birth. At diagnosis, infant hospital admission occurred in 61% of metabolic centres, mainly in Eastern, Western and Southern Europe. Breastfeeding fell sharply following diagnosis with only 30% of women still breast feeding at 6 months.53% of centres gave pre-measured Phe-free infant formula before each breast feed and 23% alternated breast feeds with Phe-free infant formula. With standard infant formula feeds, measured amounts were followed by Phe-free infant formula to satiety in 37% of centres (n = 35/95), whereas 44% (n = 42/95) advised mixing both formulas together. Weaning commenced between 17 and 26 weeks in 85% centres, ≥26 weeks in 12% and < 17 weeks in 3%.
Discussion: This is the largest European survey completed on PKU infant feeding practices. It is evident that practices varied widely across Europe, and the practicalities of infant feeding in PKU received little focus in the PKU European Guidelines (2017). There are few reports comparing different feeding techniques with blood Phe control, Phe fluctuations and growth. Controlled prospective studies are necessary to assess how different infant feeding practices may influence longer term feeding development.
Keywords: Breastfeeding; IMD, Inherited Metabolic Disorders; Infant practices; PKU, Phenylketonuria; Phe, Phenylalanine; Phe-free infant formula; Phenylalanine; Phenylketonuria.
Figures

References
-
- Bernardo H., Cesar V., W.H. Organization . 2013. Long-Term Effects of Breastfeeding: A Systematic Review.
-
- Grote V., von Kries R., Closa-Monasterolo R., Scaglioni S., Gruszfeld D., Sengier A., Langhendries J.P., Koletzko B. Protein intake and growth in the first 24 months of life. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2010;51(Suppl. 3) (S117-118) - PubMed
-
- van Wegberg A.M.J., MacDonald A., Ahring K., Belanger-Quintana A., Blau N., Bosch A.M., Burlina A., Campistol J., Feillet F., Gizewska M., Huijbregts S.C., Kearney S., Leuzzi V., Maillot F., Muntau A.C., van Rijn M., Trefz F., Walter J.H., van Spronsen F.J. The complete European guidelines on phenylketonuria: diagnosis and treatment. Orphanet J. Rare Dis. 2017;12:162. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Duncan L.L., Elder S.B. Breastfeeding the infant with PKU. J. Human Lactation. 1997;13:231–235. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

