Computed diffusion weighted imaging (cDWI) and voxelwise-computed diffusion weighted imaging (vcDWI) for oncologic liver imaging: A pilot study
- PMID: 30101156
- PMCID: PMC6084526
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ejro.2018.07.004
Computed diffusion weighted imaging (cDWI) and voxelwise-computed diffusion weighted imaging (vcDWI) for oncologic liver imaging: A pilot study
Abstract
Objective: Aim of the study was to evaluate the influence of the selection of measured b-values on the precision of cDWI in the upper abdomen as well as on the lesion contrast of PET-positive liver metastases in cDWI and vcDWI.
Methods: We performed a retrospective analysis of 10 patients (4 m, 63.5 ± 12.9 y/o) with PET-positive liver metastases examined in 3 T-PET/MRI with b = 100,600,800,1000 and 1500s/mm2. cDWI (cb1000/cb1500) and vcDWI were computed based on following combinations: i) b = 100/600 s/mm2, ii) b = 100/800 s/mm2, iii) b = 100/1000s/mm2, iv) b = 100/600/1000s/mm2 v) all measured b-values. Mean signal intensity (SI) and standard deviation (SD) in the liver, spleen, kidney, bone marrow and in liver lesions were acquired. The coefficient of variation (CV = SD/SI), the differences of SI between measured and calculated high b-value images and the lesion contrast (SI lesion/liver) were computed.
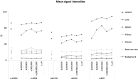
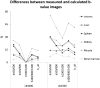
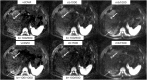
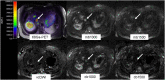
Results: With increasing upper measured b-values, the CV in cDWI and vcDWI decreased (CV in the liver in cb1500: 0.42 with b100/600 s/mm2 and 0.28 with b100/b1000s/mm2) while the differences of measured and calculated b-value images decreased (in the liver in cb1500: 30.7% with b = 100/600 s/mm2, 19.7% with b100/b1000s/mm2). In diffusion-restricted lesions, lesion contrast was at least 1.6 in cb1000 and 1.4 in cb1500, respectively, with an upper measured b-value of b = 800 s/mm2 and 2.1 for vcDWI with an upper measured b-value of b = 1000s/mm2. Overall, the lesion contrast was superior in cb1500 and vcDWI compared to cb1000 (15% and 11%, respectively).
Conclusion: Measuring higher upper b-values seems to lead to more precise computed high b-value images and a decrease of CV. vcDWI provides a comparable lesion contrast to b = 1500s/mm2 and offers additionally the reduction of T2 shine-through effects. For vcDWI, measuring b = 1000s/mm2 as upper b-value seems to be necessary to guarantee good lesion visibility in the liver based on our preliminary results.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Feasibility and Diagnostic Performance of Voxelwise Computed Diffusion-Weighted Imaging in Breast Cancer.J Magn Reson Imaging. 2019 Jun;49(6):1610-1616. doi: 10.1002/jmri.26533. Epub 2018 Oct 16. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2019. PMID: 30328211 Free PMC article.
-
Apparent diffusion coefficient-dependent voxelwise computed diffusion-weighted imaging: An approach for improving SNR and reducing T2 shine-through effects.J Magn Reson Imaging. 2016 Apr;43(4):824-32. doi: 10.1002/jmri.25044. Epub 2015 Sep 8. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2016. PMID: 26348708
-
Voxelwise computed diffusion-weighted imaging for the detection of cytotoxic oedema in brain imaging: a pilot study.Neuroradiol J. 2018 Oct;31(5):518-522. doi: 10.1177/1971400918789382. Epub 2018 Jul 17. Neuroradiol J. 2018. PMID: 30012056 Free PMC article.
-
Quantitative evaluation of computed and voxelwise computed diffusion-weighted imaging in breast cancer.Br J Radiol. 2019 Aug;92(1100):20180978. doi: 10.1259/bjr.20180978. Epub 2019 Jul 10. Br J Radiol. 2019. PMID: 31291125 Free PMC article.
-
T2-adjusted computed diffusion-weighted imaging: A novel method to enhance tumour visualisation.Comput Biol Med. 2016 Dec 1;79:92-98. doi: 10.1016/j.compbiomed.2016.09.022. Epub 2016 Oct 1. Comput Biol Med. 2016. PMID: 27770679
References
-
- Norris D.G. The effects of microscopic tissue parameters on the diffusion weighted magnetic resonance imaging experiment. NMR Biomed. 2001;14(2):77–93. - PubMed
-
- Ichikawa T., Haradome H., Hachiya J., Nitatori T., Araki T. Diffusion-weighted MR imaging with a single-shot echoplanar sequence: detection and characterization of focal hepatic lesions. AJR Am. J. Roentgenol. 1998;170(2):397–402. - PubMed
-
- Yoshikawa T., Kawamitsu H., Mitchell D.G., Ohno Y., Ku Y., Seo Y., Fujii M., Sugimura K. ADC measurement of abdominal organs and lesions using parallel imaging technique. AJR Am. J. Roentgenol. 2006;187(6):1521–1530. - PubMed
-
- Koh D.M., Collins D.J. Diffusion-weighted MRI in the body: applications and challenges in oncology. AJR Am. J. Roentgenol. 2007;188(6):1622–1635. - PubMed
-
- Padhani A.R., Koh D.M., Collins D.J. Whole-body diffusion-weighted MR imaging in cancer: current status and research directions. Radiology. 2011;261(3):700–718. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

