Blunt trauma pancreatic duct injury managed by non-operative technique, a case study and literature review
- PMID: 30101169
- PMCID: PMC6082433
- DOI: 10.1016/j.tcr.2015.03.003
Blunt trauma pancreatic duct injury managed by non-operative technique, a case study and literature review
Abstract
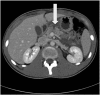
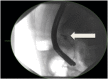
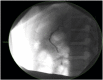
We describe the case of a 15 year old boy who presented with generalised abdominal pain following a seemingly minor collision at weekend soccer. Investigation revealed a grade IV pancreatic injury that was subsequently managed with pancreatic stent insertion by endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP) and total parenteral nutrition (TPN) prior to recommencing low fat diet 10 days post-injury.
Keywords: Blunt injury; Non-operative; Pancreas; Trauma.
Figures
References
-
- Cuenca A.G., Islam S. Paediatric pancreatic trauma: trending toward non-operative management? Am. Surg. Nov 2012;78(11):1204–1210. - PubMed
-
- Sutherland I., Ledder O., Crameri J. Pancreatic trauma in children. Pediatr. Surg. Int. Dec 2010;26(12):1201–1206. - PubMed
-
- Wood J.H., Partrick D.A., Bruny J.L., Sauaia A., Moulton S.L. Operative vs. non-operative management of blunt pancreatic trauma in children. J. Pediatr. Surg. February 2010;45(2):401–406. - PubMed
-
- Klin B., Abu-Kishk I., Jeroukhimov I. Blunt pancreatic trauma in children. Surg. Today. Jul 2011;41(7):946–954. - PubMed
-
- Rescorla F.J., Plumley D.A., Sherman S. The efficacy of early ERCP in pediatric pancreatic trauma. J. Pediatr. Surg. 1995;30:336–340. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

