Voice outcome measures after flexible endoscopic injection laryngoplasty
- PMID: 30101223
- PMCID: PMC6074013
- DOI: 10.1016/j.wjorl.2018.04.005
Voice outcome measures after flexible endoscopic injection laryngoplasty
Abstract
Objective: To report voice outcome measures after injection laryngoplasty using the transnasal or transoral flexible endoscopic technique.
Methods: A retrospective review of all patients who underwent flexible endoscopic injection laryngoplasty between June 2010 and August 2016 was carried out. Only those patients who had pre- and post-injection voice outcome measures recorded were included. Voice outcome measures recorded included perceptual voice evaluation using GRBAS, Voice Handicap Index-10 (VHI-10), maximum phonation time (MPT) and closed quotient (CQ) before and after treatment.
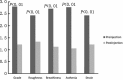
Results: Forty-six patients were identified, of which 32 had pre- and post-injection voice outcome measures recorded. There were 19 males and 13 females. The mean age was 56.97 years (range 20-86 years) and the most common indication was unilateral vocal fold paralysis. Thirteen patients had a transnasal flexible endoscopic injection), while 19 patients were injected transorally. Following injection laryngoplasty, there was significant improvement in the mean grade of dysphonia (2.81 vs. 1.22, P < 0.01, roughness (2.44 vs. 1.34, P < 0.01), breathiness (2.72 vs. 1.13, P < 0.01), asthenia (2.78 vs. 1.06, P < 0.01), and strain (2.44 vs. 1.19, P < 0.01), MPT (3.85 s vs. 9.85 s, P < 0.01) and mean CQ (0.19 vs. 0.46, P < 0.01). There was also a decrease in the mean VHI-10 score (33.31 vs. 7.94, P < 0.01).
Conclusion: s: Patients achieved significant improvement in both subjective and objective voice measures after flexible endoscopic injection laryngoplasty via the nasal or transoral route. Voice outcomes were comparable to those reported for other approaches. This technique provides an alternative approach for the management of patients with vocal fold paralysis or glottal insufficiency.
Keywords: Flexible endoscopic; Injection; Laryngoplasty; Transnasal; Transoral; Vocal fold paralysis.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Recurrent laryngeal nerve reinnervation in children: Acoustic and endoscopic characteristics pre-intervention and post-intervention. A comparison of treatment options.Laryngoscope. 2015 Dec;125 Suppl 11:S1-15. doi: 10.1002/lary.25538. Epub 2015 Aug 8. Laryngoscope. 2015. PMID: 26257068
-
Additional Injection Laryngoplasty for Patients With Unilateral Vocal Fold Paralysis.Laryngoscope. 2020 Dec;130(12):2863-2868. doi: 10.1002/lary.28567. Epub 2020 Feb 14. Laryngoscope. 2020. PMID: 32057117
-
Treatment Effects of Combined Transoral Injection Laryngoplasty with Short Voice Therapy in Patients with Unilateral Vocal Fold Immobility: A Pilot Study.Folia Phoniatr Logop. 2025 Feb 13:1-16. doi: 10.1159/000544718. Online ahead of print. Folia Phoniatr Logop. 2025. PMID: 39947149
-
Surgical interventions for pediatric unilateral vocal fold paralysis: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol. 2021 Feb;141:110553. doi: 10.1016/j.ijporl.2020.110553. Epub 2020 Dec 11. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol. 2021. PMID: 33333340
-
Vocal fold medialization-A 5-year series of single surgeon consecutive medialization with review of literature.J Eval Clin Pract. 2020 Feb;26(1):281-289. doi: 10.1111/jep.13169. Epub 2019 Jun 5. J Eval Clin Pract. 2020. PMID: 31168894 Review.
References
-
- Lewy R.B. Experience with vocal cord injection. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol. 1976;85:440–450. - PubMed
-
- Courey M.S. Injection laryngoplasty. Otolaryngol Clin N Am. 2004;37:121–138. - PubMed
-
- Upton D.C., Johnson M., Zelazny S.K., Dailey S.H. Prospective evaluation of office-based injection laryngoplasty with hyaluronic acid gel. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol. 2013;122:541–546. - PubMed
-
- Reiter R., Rudolf R., Brosch S., Sibylle B. Laryngoplasty with hyaluronic acid in patients with unilateral vocal fold paralysis. J Voice. 2012;26:785–791. - PubMed
-
- Damrose E.J. Percutaneous injection laryngoplasty in the management of acute vocal fold paralysis. Laryngoscope. 2010;120:1582–1590. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources