Global importance of RNA secondary structures in protein-coding sequences
- PMID: 30101307
- PMCID: PMC7109657
- DOI: 10.1093/bioinformatics/bty678
Global importance of RNA secondary structures in protein-coding sequences
Abstract
Motivation: The protein-coding sequences of messenger RNAs are the linear template for translation of the gene sequence into protein. Nevertheless, the RNA can also form secondary structures by intramolecular base-pairing.
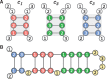
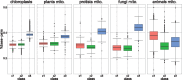
Results: We show that the nucleotide distribution within codons is biased in all taxa of life on a global scale. Thereby, RNA secondary structures that require base-pairing between the position 1 of a codon with the position 1 of an opposing codon (here named RNA secondary structure class c1) are under-represented. We conclude that this bias may result from the co-evolution of codon sequence and mRNA secondary structure, suggesting that RNA secondary structures are generally important in protein-coding regions of mRNAs. The above result also implies that codon position 2 has a smaller influence on the amino acid choice than codon position 1.
Supplementary information: Supplementary data are available at Bioinformatics online.
© The Author(s) 2018. Published by Oxford University Press. All rights reserved. For permissions, please e-mail: journals.permissions@oup.com.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Indications that "codon boundaries" are physico-chemically defined and that protein-folding information is contained in the redundant exon bases.Theor Biol Med Model. 2006 Aug 7;3:28. doi: 10.1186/1742-4682-3-28. Theor Biol Med Model. 2006. PMID: 16893453 Free PMC article.
-
New tools to analyze overlapping coding regions.BMC Bioinformatics. 2016 Dec 13;17(1):530. doi: 10.1186/s12859-016-1389-7. BMC Bioinformatics. 2016. PMID: 27964762 Free PMC article.
-
A Stem-Loop Structure in Potato Leafroll Virus Open Reading Frame 5 (ORF5) Is Essential for Readthrough Translation of the Coat Protein ORF Stop Codon 700 Bases Upstream.J Virol. 2018 May 14;92(11):e01544-17. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01544-17. Print 2018 Jun 1. J Virol. 2018. PMID: 29514911 Free PMC article.
-
The Yin and Yang of codon usage.Hum Mol Genet. 2016 Oct 1;25(R2):R77-R85. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddw207. Epub 2016 Jun 27. Hum Mol Genet. 2016. PMID: 27354349 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A systematic analysis of disease-associated variants in the 3' regulatory regions of human protein-coding genes II: the importance of mRNA secondary structure in assessing the functionality of 3' UTR variants.Hum Genet. 2006 Oct;120(3):301-33. doi: 10.1007/s00439-006-0218-x. Epub 2006 Jun 29. Hum Genet. 2006. PMID: 16807757 Review.
Cited by
-
Sulfonylation of RNA 2'-OH groups.ACS Cent Sci. 2023 Mar 1;9(3):531-539. doi: 10.1021/acscentsci.2c01237. eCollection 2023 Mar 22. ACS Cent Sci. 2023. PMID: 36968531 Free PMC article.
-
Ribosome Pausing at Inefficient Codons at the End of the Replicase Coding Region Is Important for Hepatitis C Virus Genome Replication.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Sep 22;21(18):6955. doi: 10.3390/ijms21186955. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32971876 Free PMC article.
-
Comprehensive survey of conserved RNA secondary structures in full-genome alignment of Hepatitis C virus.Sci Rep. 2024 Jul 2;14(1):15145. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-62897-0. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 38956134 Free PMC article.
-
Hepatitis C Virus Downregulates Core Subunits of Oxidative Phosphorylation, Reminiscent of the Warburg Effect in Cancer Cells.Cells. 2019 Nov 8;8(11):1410. doi: 10.3390/cells8111410. Cells. 2019. PMID: 31717433 Free PMC article. Review.
-
HCV Genetic Diversity Can Be Used to Infer Infection Recency and Time since Infection.Viruses. 2020 Oct 31;12(11):1241. doi: 10.3390/v12111241. Viruses. 2020. PMID: 33142675 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

