LipidFinder on LIPID MAPS: peak filtering, MS searching and statistical analysis for lipidomics
- PMID: 30101336
- PMCID: PMC6378932
- DOI: 10.1093/bioinformatics/bty679
LipidFinder on LIPID MAPS: peak filtering, MS searching and statistical analysis for lipidomics
Abstract
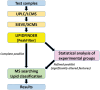
Summary: We present LipidFinder online, hosted on the LIPID MAPS website, as a liquid chromatography/mass spectrometry (LC/MS) workflow comprising peak filtering, MS searching and statistical analysis components, highly customized for interrogating lipidomic data. The online interface of LipidFinder includes several innovations such as comprehensive parameter tuning, a MS search engine employing in-house customized, curated and computationally generated databases and multiple reporting/display options. A set of integrated statistical analysis tools which enable users to identify those features which are significantly-altered under the selected experimental conditions, thereby greatly reducing the complexity of the peaklist prior to MS searching is included. LipidFinder is presented as a highly flexible, extensible user-friendly online workflow which leverages the lipidomics knowledge base and resources of the LIPID MAPS website, long recognized as a leading global lipidomics portal.
Availability and implementation: LipidFinder on LIPID MAPS is available at: http://www.lipidmaps.org/data/LF.
© The Author(s) 2018. Published by Oxford University Press.
Figures
References
-
- Katajamaa M. et al. (2006) MZmine: toolbox for processing and visualization of mass spectrometry based molecular profile data. Bioinformatics, 22, 634–636. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources