PrimedRPA: primer design for recombinase polymerase amplification assays
- PMID: 30101342
- PMCID: PMC6379019
- DOI: 10.1093/bioinformatics/bty701
PrimedRPA: primer design for recombinase polymerase amplification assays
Abstract
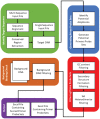
Summary: Recombinase polymerase amplification (RPA), an isothermal nucleic acid amplification method, is enhancing our ability to detect a diverse array of pathogens, thereby assisting the diagnosis of infectious diseases and the detection of microorganisms in food and water. However, new bioinformatics tools are needed to automate and improve the design of the primers and probes sets to be used in RPA, particularly to account for the high genetic diversity of circulating pathogens and cross detection of genetically similar organisms. PrimedRPA is a python-based package that automates the creation and filtering of RPA primers and probe sets. It aligns several sequences to identify conserved targets, and filters regions that cross react with possible background organisms.
Availability and implementation: PrimedRPA was implemented in Python 3 and supported on Linux and MacOS and is freely available from http://pathogenseq.lshtm.ac.uk/PrimedRPA.html.
Supplementary information: Supplementary data are available at Bioinformatics online.
© The Author(s) 2018. Published by Oxford University Press.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Graphene oxide and self-avoiding molecular recognition systems-assisted recombinase polymerase amplification coupled with lateral flow bioassay for nucleic acid detection.Mikrochim Acta. 2020 Nov 19;187(12):667. doi: 10.1007/s00604-020-04637-5. Mikrochim Acta. 2020. PMID: 33211195
-
A rapid assay for detection of Rose rosette virus using reverse transcription-recombinase polymerase amplification using multiple gene targets.J Virol Methods. 2017 Feb;240:78-84. doi: 10.1016/j.jviromet.2016.11.014. Epub 2016 Nov 30. J Virol Methods. 2017. PMID: 27915036
-
Influence of design probe and sequence mismatches on the efficiency of fluorescent RPA.World J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2019 Jun 11;35(6):95. doi: 10.1007/s11274-019-2620-2. World J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2019. PMID: 31187258
-
Recombinase polymerase amplification in the molecular diagnosis of microbiological targets and its applications.Can J Microbiol. 2022 Jun;68(6):383-402. doi: 10.1139/cjm-2021-0329. Epub 2022 Apr 8. Can J Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 35394399 Review.
-
[Recombinase Polymerase Amplification and its Applications in Parasite Detection].Zhongguo Ji Sheng Chong Xue Yu Ji Sheng Chong Bing Za Zhi. 2015 Oct;33(5):382-6. Zhongguo Ji Sheng Chong Xue Yu Ji Sheng Chong Bing Za Zhi. 2015. PMID: 26931046 Review. Chinese.
Cited by
-
3D Printed Monolithic Microreactors for Real-Time Detection of Klebsiella pneumoniae and the Resistance Gene blaNDM-1 by Recombinase Polymerase Amplification.Micromachines (Basel). 2020 Jun 17;11(6):595. doi: 10.3390/mi11060595. Micromachines (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32560308 Free PMC article.
-
RT-RPA Assay Combined with a Lateral Flow Strip to Detect Soybean Mosaic Virus.Plant Pathol J. 2024 Aug;40(4):337-345. doi: 10.5423/PPJ.OA.02.2024.0027. Epub 2024 Aug 1. Plant Pathol J. 2024. PMID: 39117333 Free PMC article.
-
The concentration of single-stranded DNA-binding proteins is a critical factor in recombinase polymerase amplification (RPA), as revealed by insights from an open-source system.PeerJ. 2025 Aug 13;13:e19758. doi: 10.7717/peerj.19758. eCollection 2025. PeerJ. 2025. PMID: 40821985 Free PMC article.
-
Schnellnachweis von SARS-CoV-2 mit recombinase polymerase amplification.Biospektrum (Heidelb). 2020;26(6):624-627. doi: 10.1007/s12268-020-1458-3. Epub 2020 Oct 14. Biospektrum (Heidelb). 2020. PMID: 33078045 Free PMC article. Review. German.
-
Recombinase Polymerase Amplification (RPA) Combined with Lateral Flow Immunoassay for Rapid Detection of Salmonella in Food.Foods. 2019 Dec 26;9(1):27. doi: 10.3390/foods9010027. Foods. 2019. PMID: 31887998 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- MR/K000551/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- BB_/Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council/United Kingdom
- MR/M01360X/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- MR/R020973/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- MR/N010469/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources