Benzoxazole derivatives: design, synthesis and biological evaluation
- PMID: 30101384
- PMCID: PMC6087707
- DOI: 10.1186/s13065-018-0459-5
Benzoxazole derivatives: design, synthesis and biological evaluation
Abstract
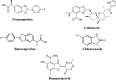
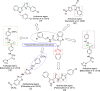
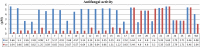
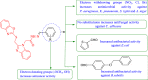
Background: A new series of benzoxazole analogues was synthesized and checked for their in vitro antibacterial, antifungal and anticancer activities.
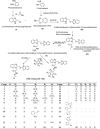
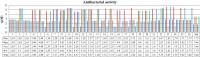
Results and discussion: The synthesized benzoxazole compounds were confirmed by IR, 1H/13C-NMR, mass and screened for their in vitro antimicrobial activity against Gram-positive bacterium: Bacillus subtilis, four Gram-negative bacteria: Escherichia coli, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Klebsiella pneumoniae, Salmonella typhi and two fungal strains: Candida albicans and Aspergillus niger using tube dilution technique and minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) was noted in µM and compared to ofloxacin and fluconazole. Human colorectal carcinoma (HCT116) cancer cell line was used for the determination of in vitro anticancer activity (IC50 value) by Sulforhodamine B assay using 5-fluorouracil as standard drug.
Conclusion: The performed study indicated that the compounds 1, 10, 13, 16, 19, 20 and 24 had highest antimicrobial activity with MIC values comparable to ofloxacin and fluconazole and compounds 4, 6, 25 and 26 had best anticancer activity in comparison to 5-fluorouracil.
Keywords: Anticancer; Antimicrobial; Benzoxazole; Characterization; Synthesis.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Bis-pyrimidine acetamides: design, synthesis and biological evaluation.Chem Cent J. 2017 Aug 8;11(1):80. doi: 10.1186/s13065-017-0312-2. Chem Cent J. 2017. PMID: 29086907 Free PMC article.
-
Design, synthesis and therapeutic potential of 3-(2-(1H-benzo[d]imidazol-2-ylthio)acetamido)-N-(substituted phenyl)benzamide analogues.Chem Cent J. 2018 Dec 19;12(1):139. doi: 10.1186/s13065-018-0513-3. Chem Cent J. 2018. PMID: 30569392 Free PMC article.
-
Design, Synthesis, SAR Study, Antimicrobial and Anticancer Evaluation of Novel 2-Mercaptobenzimidazole Azomethine Derivatives.Mini Rev Med Chem. 2020;20(15):1559-1571. doi: 10.2174/1389557518666180903151849. Mini Rev Med Chem. 2020. PMID: 30179132
-
Synthesis of thiophene derivatives and their anti-microbial, antioxidant, anticorrosion and anticancer activity.BMC Chem. 2019 Apr 18;13(1):54. doi: 10.1186/s13065-019-0569-8. eCollection 2019 Dec. BMC Chem. 2019. PMID: 31384802 Free PMC article.
-
Design, synthesis and antimicrobial evaluation of pyrimidin-2-ol/thiol/amine analogues.Chem Cent J. 2017 Jun 9;11(1):52. doi: 10.1186/s13065-017-0284-2. Chem Cent J. 2017. PMID: 29086852 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Biological activity of 3-(2-benzoxazol-5-yl)alanine derivatives.Amino Acids. 2021 Aug;53(8):1257-1268. doi: 10.1007/s00726-021-03030-7. Epub 2021 Jul 8. Amino Acids. 2021. PMID: 34240252 Free PMC article.
-
Design, synthesis, anticancer evaluation and molecular docking studies of 1,2,3-triazole incorporated 1,3,4-oxadiazole-Triazine derivatives.Heliyon. 2023 May 3;9(5):e15935. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e15935. eCollection 2023 May. Heliyon. 2023. PMID: 37206039 Free PMC article.
-
Antibacterial Activity and Antifungal Activity of Monomeric Alkaloids.Toxins (Basel). 2024 Nov 12;16(11):489. doi: 10.3390/toxins16110489. Toxins (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39591244 Free PMC article. Review.
-
An Insight into Rational Drug Design: The Development of In-House Azole Compounds with Antimicrobial Activity.Antibiotics (Basel). 2024 Aug 13;13(8):763. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics13080763. Antibiotics (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39200063 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Design, synthesis and in silico screening of benzoxazole-thiazolidinone hybrids as potential inhibitors of SARS-CoV-2 proteases.RSC Adv. 2021 Dec 10;11(62):39328-39342. doi: 10.1039/d1ra07504g. eCollection 2021 Dec 6. RSC Adv. 2021. PMID: 35492479 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Chilumula NR, Gudipati R, Ampati S, Manda S, Gadhe D. Synthesis of some novel methyl-2-(2-(arylideneamino)oxazol-4-ylamino)benzoxazole-5-carboxylate derivatives as antimicrobial agents. Int J Chem Res. 2010;1(2):1–6.
-
- Ram Prasad S, Saraswathy T, Niraimathi V, Indhumathi B. Synthesis, characterization and antimicrobial activity of some hetero benzocaine dervivatives. Int J Pharm Pharm Sci. 2012;4(5):285–287.
-
- Kamal A, Dastagiri D, Ramaiah MJ, Reddy JS, Bharathi EV, Reddy MK, Sagar MP, Reddy TL, Pushpavalli S, Bhadra MP. Synthesis and apoptosis inducing ability of new anilino substituted pyrimidine sulfonamides as potential anticancer agents. Eur J Med Chem. 2011;46(12):5817–5824. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2011.09.039. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

