Regional expression of tyrosinase in central catecholaminergic systems of colored mice
- PMID: 30101816
- PMCID: PMC6389515
- DOI: 10.1538/expanim.18-0053
Regional expression of tyrosinase in central catecholaminergic systems of colored mice
Abstract
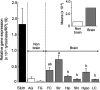
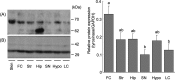
A relationship between coat color and behavioral characteristics has been reported for numerous species. We previously indicated that particular behavioral traits contributing to the genotype at the agouti locus manifest only when possessing a wild-type allele at the albino (i.e., tyrosinase: Tyr) locus. The present study was performed to investigate tyrosinase expression with marked activity in central nervous systems. The whole brain of male B10 and B10-c mice, a B10 congenic strain of the albino locus from BALB/c, at 8 to 9 weeks of age was removed, and obtained several regions of brain, especially catecholaminergic. Comparatively large amounts of Tyr mRNA and its translation products of approximately 68 kDa were found in the regions obtained, and definitely possessed the enzyme activity for the oxidation of L-tyrosine. The present results indicate the possibility that the amount of catecholamines produced in albino mice is higher than that of colored mice due to the deficit in tyrosinase heritably.
Keywords: albino; central nervous system; striatum; tyrosinase.
Figures



References
-
- Branza-Nichita N., Negroiu G., Petrescu A.J., Garman E.F., Platt F.M., Wormald M.R., Dwek R.A., Petrescu S.M.2000. Mutations at critical N-glycosylation sites reduce tyrosinase activity by altering folding and quality control. J. Biol. Chem. 275: 8169–8175. doi: 10.1074/jbc.275.11.8169 - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

