Massively parallel sequencing techniques for forensics: A review
- PMID: 30101986
- PMCID: PMC6282972
- DOI: 10.1002/elps.201800082
Massively parallel sequencing techniques for forensics: A review
Abstract
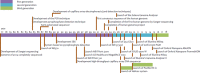
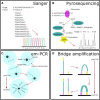
DNA sequencing, starting with Sanger's chain termination method in 1977 and evolving into the next generation sequencing (NGS) techniques of today that employ massively parallel sequencing (MPS), has become essential in application areas such as biotechnology, virology, and medical diagnostics. Reflected by the growing number of articles published over the last 2-3 years, these techniques have also gained attention in the forensic field. This review contains a brief description of first, second, and third generation sequencing techniques, and focuses on the recent developments in human DNA analysis applicable in the forensic field. Relevance to the forensic analysis is that besides generation of standard STR-profiles, DNA repeats can also be sequenced to look for polymorphisms. Furthermore, additional SNPs can be sequenced to acquire information on ancestry, paternity or phenotype. The current MPS systems are also very helpful in cases where only a limited amount of DNA or highly degraded DNA has been secured from a crime scene. If enough autosomal DNA is not present, mitochondrial DNA can be sequenced for maternal lineage analysis. These developments clearly demonstrate that the use of NGS will grow into an indispensable tool for forensic science.
Keywords: DNA analysis; Forensics; Massively parallel sequencing; Short tandem repeat; Single nucleotide polymorphism.
© 2018 The Authors. Electrophoresis Published by Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Application Progress of Massively Parallel Sequencing Technology in STR Genetic Marker Detection.Fa Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2022 Apr 25;38(2):267-279. doi: 10.12116/j.issn.1004-5619.2020.500502. Fa Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2022. PMID: 35899518 Review. Chinese, English.
-
Massively parallel sequencing of 17 commonly used forensic autosomal STRs and amelogenin with small amplicons.Forensic Sci Int Genet. 2016 May;22:1-7. doi: 10.1016/j.fsigen.2016.01.001. Epub 2016 Jan 8. Forensic Sci Int Genet. 2016. PMID: 26799314
-
Massively parallel sequencing of forensic STRs: Considerations of the DNA commission of the International Society for Forensic Genetics (ISFG) on minimal nomenclature requirements.Forensic Sci Int Genet. 2016 May;22:54-63. doi: 10.1016/j.fsigen.2016.01.009. Epub 2016 Jan 21. Forensic Sci Int Genet. 2016. PMID: 26844919
-
Forensic STR and SNP Genotyping of Formalin-Fixed Skeleton Samples With Illumina's ForenSeq System.Electrophoresis. 2024 Nov;45(21-22):2019-2027. doi: 10.1002/elps.202400056. Epub 2024 Oct 14. Electrophoresis. 2024. PMID: 39402849
-
Current state-of-art of STR sequencing in forensic genetics.Electrophoresis. 2018 Nov;39(21):2655-2668. doi: 10.1002/elps.201800030. Epub 2018 Jun 4. Electrophoresis. 2018. PMID: 29750373 Review.
Cited by
-
DNA Sequencing Methods: From Past to Present.Eurasian J Med. 2022 Dec;54(Suppl1):47-56. doi: 10.5152/eurasianjmed.2022.22280. Eurasian J Med. 2022. PMID: 36655445 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of Skeletal Remains Using Genetic Profiling: A Case Linking Italy and Poland.Genes (Basel). 2023 Jan 3;14(1):134. doi: 10.3390/genes14010134. Genes (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36672875 Free PMC article.
-
Eye and Hair Color Prediction of Ancient and Second World War Skeletal Remains Using a Forensic PCR-MPS Approach.Genes (Basel). 2022 Aug 12;13(8):1432. doi: 10.3390/genes13081432. Genes (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36011343 Free PMC article.
-
Recombulator-X: A fast and user-friendly tool for estimating X chromosome recombination rates in forensic genetics.PLoS Comput Biol. 2023 Sep 18;19(9):e1011474. doi: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1011474. eCollection 2023 Sep. PLoS Comput Biol. 2023. PMID: 37721960 Free PMC article.
-
An ELOVL2-Based Epigenetic Clock for Forensic Age Prediction: A Systematic Review.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Jan 23;24(3):2254. doi: 10.3390/ijms24032254. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36768576 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Liu, L. , Li, Y. , Li, S. , Hu, N. , He, Y. , Lin, D. , Lu, L. , Law, M. , BioMed Res. Int. 2012, 2012, http://doi.org.10.1155/2012/251364.
-
- Kircher, M. , Kelso, J. , Bioessays 2010, 32, 524–536. - PubMed
-
- Van Dijk, E. L. , Auger, H. , Jaszczyszyn, Y. , Thermes, C. , Trends Genet. 2014, 30, 418–426. - PubMed
-
- Ansorge, W. J. , New Biotechnol. 2009, 25, 195–203. - PubMed
-
- Kchouk, M. , Gibrat, J.‐F. , Elloumi, M. , Biol. Med. (Aligarh) 2017, 9, 395.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

