CD28 blockade controls T cell activation to prevent graft-versus-host disease in primates
- PMID: 30102255
- PMCID: PMC6118599
- DOI: 10.1172/JCI98793
CD28 blockade controls T cell activation to prevent graft-versus-host disease in primates
Abstract
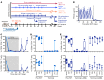
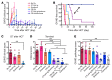
Controlling graft-versus-host disease (GVHD) remains a major unmet need in stem cell transplantation, and new, targeted therapies are being actively developed. CD28-CD80/86 costimulation blockade represents a promising strategy, but targeting CD80/CD86 with CTLA4-Ig may be associated with undesired blockade of coinhibitory pathways. In contrast, targeted blockade of CD28 exclusively inhibits T cell costimulation and may more potently prevent GVHD. Here, we investigated FR104, an antagonistic CD28-specific pegylated-Fab', in the nonhuman primate (NHP) GVHD model and completed a multiparameter interrogation comparing it with CTLA4-Ig, with and without sirolimus, including clinical, histopathologic, flow cytometric, and transcriptomic analyses. We document that FR104 monoprophylaxis and combined prophylaxis with FR104/sirolimus led to enhanced control of effector T cell proliferation and activation compared with the use of CTLA4-Ig or CTLA4-Ig/sirolimus. Importantly, FR104/sirolimus did not lead to a beneficial impact on Treg reconstitution or homeostasis, consistent with control of conventional T cell activation and IL-2 production needed to support Tregs. While FR104/sirolimus had a salutary effect on GVHD-free survival, overall survival was not improved, due to death in the absence of GVHD in several FR104/sirolimus recipients in the setting of sepsis and a paralyzed INF-γ response. These results therefore suggest that effectively deploying CD28 in the clinic will require close scrutiny of both the benefits and risks of extensively abrogating conventional T cell activation after transplant.
Keywords: Bone marrow transplantation; Immunology; Transplantation.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures







Similar articles
-
GVHD after haploidentical transplantation: a novel, MHC-defined rhesus macaque model identifies CD28- CD8+ T cells as a reservoir of breakthrough T-cell proliferation during costimulation blockade and sirolimus-based immunosuppression.Blood. 2010 Dec 9;116(24):5403-18. doi: 10.1182/blood-2010-06-289272. Epub 2010 Sep 10. Blood. 2010. PMID: 20833977 Free PMC article.
-
In vivo blockade of CD28/CTLA4: B7/BB1 interaction with CTLA4-Ig reduces lethal murine graft-versus-host disease across the major histocompatibility complex barrier in mice.Blood. 1994 Jun 15;83(12):3815-25. Blood. 1994. PMID: 7515723
-
Selective blockade of CD28-mediated T cell costimulation protects rhesus monkeys against acute fatal experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis.J Immunol. 2015 Feb 15;194(4):1454-66. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1402563. Epub 2015 Jan 14. J Immunol. 2015. PMID: 25589073
-
T-cell co-signalling molecules in graft-versus-host disease.Ann Hematol. 2000 Jun;79(6):283-90. doi: 10.1007/s002779900134. Ann Hematol. 2000. PMID: 10901605 Review.
-
Challenges and opportunities in targeting the CD28/CTLA-4 pathway in transplantation and autoimmunity.Expert Opin Biol Ther. 2017 Aug;17(8):1001-1012. doi: 10.1080/14712598.2017.1333595. Epub 2017 May 30. Expert Opin Biol Ther. 2017. PMID: 28525959 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Costimulation blockade in combination with IL-2 permits regulatory T cell sparing immunomodulation that inhibits autoimmunity.Nat Commun. 2022 Nov 9;13(1):6757. doi: 10.1038/s41467-022-34477-1. Nat Commun. 2022. PMID: 36347877 Free PMC article.
-
Current Concepts and Advances in Graft-Versus-Host Disease Immunology.Annu Rev Immunol. 2021 Apr 26;39:19-49. doi: 10.1146/annurev-immunol-102119-073227. Epub 2021 Jan 11. Annu Rev Immunol. 2021. PMID: 33428454 Free PMC article.
-
Abatacept for acute graft-versus-host disease prophylaxis after unrelated donor hematopoietic cell transplantation.Blood. 2024 Oct 24;144(17):1834-1845. doi: 10.1182/blood.2023023660. Blood. 2024. PMID: 39028876
-
Abatacept is effective as GVHD prophylaxis in unrelated donor stem cell transplantation for children with severe sickle cell disease.Blood Adv. 2020 Aug 25;4(16):3894-3899. doi: 10.1182/bloodadvances.2020002236. Blood Adv. 2020. PMID: 32813873 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
CRISPR/Cas9 deletion of MIR155HG in human T cells reduces incidence and severity of acute GVHD in a xenogeneic model.Blood Adv. 2024 Feb 27;8(4):947-958. doi: 10.1182/bloodadvances.2023010570. Blood Adv. 2024. PMID: 38181781 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Wagner JE, Thompson JS, Carter SL, Kernan NA, Unrelated Donor Marrow Transplantation Trial Effect of graft-versus-host disease prophylaxis on 3-year disease-free survival in recipients of unrelated donor bone marrow (T-cell Depletion Trial): a multi-centre, randomised phase II-III trial. Lancet. 2005;366(9487):733–741. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(05)66996-6. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Rizzo JD, et al. Recommended screening and preventive practices for long-term survivors after hematopoietic cell transplantation: joint recommendations of the European Group for Blood and Marrow Transplantation, Center for International Blood and Marrow Transplant Research, and the American Society for Blood and Marrow Transplantation (EBMT/CIBMTR/ASBMT) Bone Marrow Transplant. 2006;37(3):249–261. doi: 10.1038/sj.bmt.1705243. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

