Alpha-Synuclein Modulates the Physical Properties of DNA
- PMID: 30102440
- PMCID: PMC6217799
- DOI: 10.1002/chem.201803933
Alpha-Synuclein Modulates the Physical Properties of DNA
Abstract
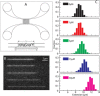
Fundamental research on Parkinson's disease (PD) most often focuses on the ability of α-synuclein (aS) to form oligomers and amyloids, and how such species promote brain cell death. However, there are indications that aS also plays a gene-regulatory role in the cell nucleus. Here, the interaction between monomeric aS and DNA in vitro has been investigated with single-molecule techniques. Using a nanofluidic channel system, it was discovered that aS binds to DNA and by studying the DNA-protein complexes at different confinements we determined that aS binding increases the persistence length of DNA from 70 to 90 nm at high coverage. By atomic force microscopy it was revealed that at low protein-to-DNA ratio, the aS binding occurs as small protein clusters scattered along the DNA; at high protein-to-DNA ratio, the DNA is fully covered by protein. As DNA-aS interactions may play roles in PD, it is of importance to characterize biophysical properties of such complexes in detail.
Keywords: DNA; biochemistry; nanofluidics; proteins; synuclein.
© 2018 The Authors. Published by Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA.
Figures


References
-
- Pringsheim T., Jette N., Frolkis A., Steeves T. D., Mov. Disord. 2014, 29, 1583–1590. - PubMed
-
- None
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

