Enhancing Osteosarcoma Killing and CT Imaging Using Ultrahigh Drug Loading and NIR-Responsive Bismuth Sulfide@Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles
- PMID: 30102469
- PMCID: PMC6504251
- DOI: 10.1002/adhm.201800602
Enhancing Osteosarcoma Killing and CT Imaging Using Ultrahigh Drug Loading and NIR-Responsive Bismuth Sulfide@Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles
Erratum in
-
Enhancing Osteosacoma Killing and CT Imaging Using Ultra High Drug Loading and NIR-Responsive Bismuth Sulfide @Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles.Adv Healthc Mater. 2024 Apr;13(10):e2304500. doi: 10.1002/adhm.202304500. Epub 2024 Mar 9. Adv Healthc Mater. 2024. PMID: 38459806 No abstract available.
Abstract
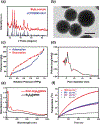
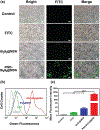
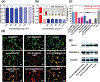
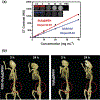
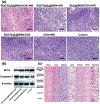
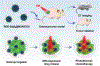
Despite its 5-year event-free survival rate increasing to 60-65% due to surgery and chemotherapy, osteosarcoma (OS) remains one of the most threatening malignant human tumors, especially in young patients. Therefore, a new approach that combines early diagnosis with efficient tumor eradication and bioimaging is urgently needed. Here, a new type of mesoporous silica-coated bismuth sulfide nanoparticles (Bi2 S3 @MSN NPs) is developed. The well distributed mesoporous pores and large surface areas hold great promise for drug protection and encapsulation (doxorubicin (DOX), 99.85%). Moreover, the high photothermal efficiency of Bi2 S3 @MSNs (36.62%) offers great possibility for cancer synergistic treatment and highly near-infrared-triggered drug release (even at an ultralow power density of 0.3 W cm-2 ). After covalently conjugated to arginine-glycine-aspartic acid (RGD) peptide [c(RGDyC)], the NPs exhibit a high specificity for osteosarcoma and finally accumulate in the tumor cells (tenfold more than peritumoral tissues) for computed tomography (CT) imaging and tumor ablation. Importantly, the synergistic photothermal therapy-chemotherapy of the RGD-Bi2 S3 @MSN/DOX significantly ablates the highly malignant OS. It is further proved that the superior combined killing effect is achieved by activating the mitochondrial apoptosis pathway. Hence, the smart RGD-Bi2 S3 @MSN/DOX theranostic platform is a promising candidate for future applications in CT monitoring and synergistic treatment of malignant tumors.
Keywords: Bi2S3@MSN; X-ray computed tomography; mitochondrial apoptosis pathway; osteosarcoma; photothermal therapy-chemotherapy.
© 2018 WILEY-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA, Weinheim.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Kansara M, Teng MW, Smyth MJ, Thomas DM, Nat. Rev Cancer 2014, 14, 722. - PubMed
-
- Ma H, Jiang C, Zhai D, Luo Y, Chen Y, Lv F, Yi Z, Deng Y, Wang J, Chang J, Adv. Funct. Mater. 2016, 26, 1197.
-
- Jaque D, Martinez Maestro L, del Rosal B, Haro-Gonzalez P, Benayas A, Plaza JL, Martin Rodriguez E, Garcia Sole J, Nanoscale 2014, 6, 9494. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

