Theranostics in neuroendocrine tumours: somatostatin receptor imaging and therapy
- PMID: 30102557
- PMCID: PMC6475945
- DOI: 10.1259/bjr.20180108
Theranostics in neuroendocrine tumours: somatostatin receptor imaging and therapy
Abstract
Theranostics and its principles: pre-treatment selection of patients who are most likely to benefit from treatment by the use of a related, specific diagnostic test are integral to the treatment of patients with neuroendocrine tumours (NETs). This is due to NETs' important, but variable, somatostatin receptor (SSTR) expression, their heterogeneity and variation in site of primary and rate of progression. Only patients whose tumours have sufficient expression of SSTRs will benefit from SSTR-based radionuclide therapy and demonstrating this expression prior to therapy is essential. This article provides a relevant overview of NETs and the multiple facets of SSTR based theranostics, including imaging and therapy radionuclides; clinical efficacy and toxicity; patient selection and treatment and finally emerging radiopharmaceuticals and newer clinical applications.
Figures
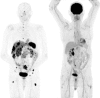
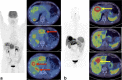
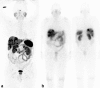

Similar articles
-
Theranostics in Neuroendocrine Tumors: Updates and Emerging Technologies.Curr Probl Cancer. 2024 Oct;52:101129. doi: 10.1016/j.currproblcancer.2024.101129. Epub 2024 Sep 3. Curr Probl Cancer. 2024. PMID: 39232443 Review.
-
Tumor imaging and therapy using radiolabeled somatostatin analogues.Acc Chem Res. 2009 Jul 21;42(7):873-80. doi: 10.1021/ar800188e. Acc Chem Res. 2009. PMID: 19445476
-
68Gallium- and 90Yttrium-/ 177Lutetium: "theranostic twins" for diagnosis and treatment of NETs.Ann Nucl Med. 2015 Jan;29(1):1-7. doi: 10.1007/s12149-014-0898-6. Epub 2014 Aug 20. Ann Nucl Med. 2015. PMID: 25139472 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Patient selection for personalized peptide receptor radionuclide therapy using Ga-68 somatostatin receptor PET/CT.PET Clin. 2014 Jan;9(1):83-90. doi: 10.1016/j.cpet.2013.08.015. PET Clin. 2014. PMID: 25029937 Review.
-
The theranostic promise for Neuroendocrine Tumors in the late 2010s - Where do we stand, where do we go?Theranostics. 2018 Nov 29;8(22):6088-6100. doi: 10.7150/thno.30357. eCollection 2018. Theranostics. 2018. PMID: 30613284 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Immunohistochemical Expression of Somatostatin Receptor Subtypes in a Panel of Neuroendocrine Neoplasias.J Histochem Cytochem. 2019 Oct;67(10):735-743. doi: 10.1369/0022155419856900. Epub 2019 Jun 10. J Histochem Cytochem. 2019. PMID: 31381461 Free PMC article.
-
The Role of Somatostatin in the Gastrointestinal Tract.Biology (Basel). 2025 May 16;14(5):558. doi: 10.3390/biology14050558. Biology (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40427747 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Actinium-225 Targeted Agents: Where Are We Now?Brachytherapy. 2023 Nov-Dec;22(6):697-708. doi: 10.1016/j.brachy.2023.06.228. Epub 2023 Sep 9. Brachytherapy. 2023. PMID: 37690972 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Combined use of 177Lu-DOTATATE and metronomic capecitabine (Lu-X) in FDG-positive gastro-entero-pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors.Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2021 Sep;48(10):3260-3267. doi: 10.1007/s00259-021-05236-z. Epub 2021 Feb 18. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2021. PMID: 33604690 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Expanding Theranostic Radiopharmaceuticals for Tumor Diagnosis and Therapy.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2021 Dec 22;15(1):13. doi: 10.3390/ph15010013. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2021. PMID: 35056071 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Pape UF, Perren A, Niederle B, Gross D, Gress T, Costa F, et al. . ENETS Consensus Guidelines for the management of patients with neuroendocrine neoplasms from the jejuno-ileum and the appendix including goblet cell carcinomas. Neuroendocrinology 2012; 95: 135–56. doi: 10.1159/000335629 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Cives M, Strosberg J. An update on gastroenteropancreatic neuroendocrine tumors. Oncology 2014; 28: 749–56. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

