Micro-RNA-137 Inhibits Tau Hyperphosphorylation in Alzheimer's Disease and Targets the CACNA1C Gene in Transgenic Mice and Human Neuroblastoma SH-SY5Y Cells
- PMID: 30102687
- PMCID: PMC6104547
- DOI: 10.12659/MSM.908765
Micro-RNA-137 Inhibits Tau Hyperphosphorylation in Alzheimer's Disease and Targets the CACNA1C Gene in Transgenic Mice and Human Neuroblastoma SH-SY5Y Cells
Abstract
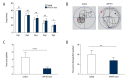
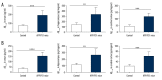
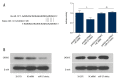
BACKGROUND Alzheimer's disease (AD) results in cognitive impairment. The calcium voltage-gated channel subunit alpha-1 C CACNA1C gene encodes an alpha-1 C subunit of L-type calcium channel (LTCC). The aim of this study was to investigate the role of micro-RNA-137 (miR-137) and the CACNA1C gene in APPswe/PS1ΔE9 (APP/PS1) double-transgenic AD mice and in human neuroblastoma SH-SY5Y cells. MATERIAL AND METHODS Six-month-old APP/PS1 double-transgenic AD mice (N=6) and age-matched normal C57BL/6 mice (N=6) underwent a Morris water maze (MWM) test, expression levels of amyloid-β (Aβ), LTCC, the CACNA1C gene, and miR-137 were measured in the rat hippocampus and cerebral cortex in both groups of mice. A luciferase assay was used to evaluate the effect of miR-137 on the expression of CACNA1C in SH-SY5Y human neuroblastoma SH-SY5Y cells. Western blotting was used to detect the CACNA1C, phosphorylated-tau (p-tau), and Aβ proteins. RESULTS In APP/PS1 transgenic AD mice, spatial learning and memory was significantly reduced, levels of Aβ1-40 and Aβ1-42 were increased in the serum, hippocampus, and cerebral cortex, expression levels of miR-137 were reduced, expression of CACNA1C protein was increased in the hippocampus and cerebral cortex, compared with normal control mice. miR-137 regulated the expression of the CACNA1C gene. Increased expression levels of p-tau (Ser202, Ser396, and Ser404) induced by Aβ1-42 were inhibited by miR-137 mimics in SH-SY5Y human neuroblastoma cells in vitro. CONCLUSIONS In a transgenic mouse model of AD, miR-137 and expression of the CACNA1C gene inhibited the hyperphosphorylation of tau protein.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Long non-coding RNA 00507/miRNA-181c-5p/TTBK1/MAPT axis regulates tau hyperphosphorylation in Alzheimer's disease.J Gene Med. 2020 Dec;22(12):e3268. doi: 10.1002/jgm.3268. Epub 2020 Sep 23. J Gene Med. 2020. PMID: 32891070
-
miR-106b inhibits tau phosphorylation at Tyr18 by targeting Fyn in a model of Alzheimer's disease.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2016 Sep 16;478(2):852-7. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2016.08.037. Epub 2016 Aug 9. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2016. PMID: 27520374
-
Atorvastatin ameliorates cognitive impairment, Aβ1-42 production and Tau hyperphosphorylation in APP/PS1 transgenic mice.Metab Brain Dis. 2016 Jun;31(3):693-703. doi: 10.1007/s11011-016-9803-4. Epub 2016 Feb 16. Metab Brain Dis. 2016. PMID: 26883430
-
Effects of CX3CR1 and Fractalkine Chemokines in Amyloid Beta Clearance and p-Tau Accumulation in Alzheimer's Disease (AD) Rodent Models: Is Fractalkine a Systemic Biomarker for AD?Curr Alzheimer Res. 2016;13(4):403-12. doi: 10.2174/1567205013666151116125714. Curr Alzheimer Res. 2016. PMID: 26567742 Review.
-
MicroRNA-455-5p/CPEB1 pathway mediates Aβ-related learning and memory deficits in a mouse model of Alzheimer's disease.Brain Res Bull. 2021 Dec;177:282-294. doi: 10.1016/j.brainresbull.2021.10.008. Epub 2021 Oct 20. Brain Res Bull. 2021. PMID: 34678444 Review.
Cited by
-
The Role of miR-137 in Neurodegenerative Disorders.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Jun 30;25(13):7229. doi: 10.3390/ijms25137229. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39000336 Free PMC article. Review.
-
MicroRNA Expression Signature in Mild Cognitive Impairment Due to Alzheimer's Disease.Mol Neurobiol. 2020 Nov;57(11):4408-4416. doi: 10.1007/s12035-020-02029-7. Epub 2020 Jul 31. Mol Neurobiol. 2020. PMID: 32737762 Free PMC article.
-
miRNA-137-5p improves spatial memory and cognition in Alzheimer's mice by targeting ubiquitin-specific peptidase 30.Animal Model Exp Med. 2023 Dec;6(6):526-536. doi: 10.1002/ame2.12368. Epub 2023 Dec 18. Animal Model Exp Med. 2023. PMID: 38111333 Free PMC article.
-
Curcumin prevents Alzheimer's disease progression by upregulating JMJD3.Am J Transl Res. 2022 Aug 15;14(8):5280-5294. eCollection 2022. Am J Transl Res. 2022. PMID: 36105064 Free PMC article.
-
Circ_0049472 regulates the damage of Aβ-induced SK-N-SH and CHP-212 cells by mediating the miR-107/KIF1B axis.Exp Brain Res. 2022 Sep;240(9):2299-2309. doi: 10.1007/s00221-022-06401-y. Epub 2022 Jul 26. Exp Brain Res. 2022. PMID: 35881155
References
-
- Alzheimer’s Association. 2014 Alzheimer’s disease facts and figures. Alzheimers Dement. 2014;10:e47–92. - PubMed
-
- Danborg PB, Simonsen AH, Waldemar G, Heegaard NH. The potential of microRNAs as biofluid markers of neurodegenerative diseases: A systematic review. Biomarkers. 2014;19:259–68. - PubMed
-
- Querfurth HW, Laferla FM. Alzheimer’s disease. N Engl J Med. 2010;362:329–44. - PubMed
-
- Reddy PH, Mcweeney S. Mapping cellular transcriptosomes in autopsied Alzheimer’s disease subjects and relevant animal models. Neurobiol Aging. 2006;27:1060–77. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

