Histone Deacetylase Inhibitor Suberanilohydroxamic Acid Treatment Reverses Hyposensitivity to γ-Aminobutyric Acid in the Ventral Tegmental Area During Ethanol Withdrawal
- PMID: 30103280
- PMCID: PMC6214766
- DOI: 10.1111/acer.13870
Histone Deacetylase Inhibitor Suberanilohydroxamic Acid Treatment Reverses Hyposensitivity to γ-Aminobutyric Acid in the Ventral Tegmental Area During Ethanol Withdrawal
Abstract
Background: The ventral tegmental area (VTA) is important for alcohol-related reward and reinforcement. Mouse VTA neurons are hyposensitive to γ-aminobutyric acid (GABA) during ethanol (EtOH) withdrawal, and GABA responsiveness is normalized by in vitro treatment with histone deacetylase inhibitors (HDACi). The present study examined the effect of a systemically administered HDACi, suberanilohydroxamic acid (SAHA) on GABA sensitivity, and related molecular changes in VTA neurons during withdrawal after chronic EtOH intake in rats.
Methods: Sprague Dawley male adult rats were fed with Lieber-DeCarli diet (9% EtOH or control diet) for 16 days. Experimental groups included control diet-fed and EtOH diet-fed (0- or 24-hour withdrawal) rats treated with either SAHA or vehicle injection. Single-unit recordings were used to measure the response of VTA neurons to GABA. Immunohistochemistry was performed to examine levels of HDAC2, acetylated histone H3 lysine 9 (acH3K9), and GABAA receptor α1 and α5 subunits in the VTA; quantitative polymerase chain reaction was performed to examine the mRNA levels of HDAC2 and GABAA receptor subunits.
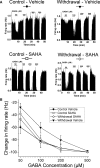
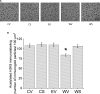
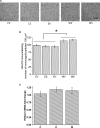
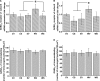
Results: VTA neurons from the withdrawal group exhibited GABA hyposensitivity. In vivo SAHA treatment 2 hours before sacrifice normalized the sensitivity of VTA neurons to GABA. EtOH withdrawal was associated with increased HDAC2 and decreased acH3K9 protein levels; SAHA treatment normalized acH3K9 levels. Interestingly, no significant change was observed in the mRNA levels of HDAC2. The mRNA levels, but not protein levels, of GABAA receptor α1 and α5 subunits were increased during withdrawal.
Conclusions: Withdrawal from chronic EtOH exposure results in a decrease in GABA-mediated inhibition, and this GABA hyposensitivity is normalized by in vivo SAHA treatment. Disruption of signaling in the VTA produced by alteration of GABA neurotransmission could be 1 neuroadaptive physiological process leading to craving and relapse. These results suggest that HDACi pharmacotherapy with agents like SAHA might be an effective treatment for alcoholism.
Keywords: SAHA; VTA; Dopamine; Epigenetic; Ethanol.
© 2018 The Authors. Alcoholism: Clinical & Experimental Research published by Wiley Periodicals, Inc. on behalf of Research Society on Alcoholism.
Figures
References
-
- Albanese A, Minciacchi D (1983) Organization of the ascending projections from the ventral tegmental area: a multiple fluorescent retrograde tracer study in the rat. J Comp Neurol 216:406–420. - PubMed
-
- Bailey CP, O'Callaghan MJ, Croft AP, Manley SJ, Little HJ (2001) Alterations in mesolimbic dopamine function during the abstinence period following chronic ethanol consumption. Neuropharmacology 41:989–999. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

