The Substituent Effect on the Radical Scavenging Activity of Apigenin
- PMID: 30103379
- PMCID: PMC6222755
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules23081989
The Substituent Effect on the Radical Scavenging Activity of Apigenin
Abstract
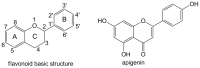
Flavonoids widely found in natural foods are excellent free radical scavengers. The relationship between the substituent and antioxidative activity of flavonoids has not yet been completely elucidated. In this work, the antioxidative activity of apigenin derivatives with different substituents at the C3 position was determined by density functional theory (DFT) calculations. The bond dissociation enthalpy (BDE), ionization potential (IP), and proton affinity (PA) were calculated. Donator acceptor map (DAM) analysis illustrated that the studied compounds are worse electron acceptors than F and also are not better electron donors than Na. The strongest antioxidative group of apigenin derivatives was the same as apigenin. Excellent correlations were found between the BDE/IP/PA and Hammett sigma constants. Therefore, Hammett sigma constants can be used to predict the antioxidative activity of substituted apigenin and to design new antioxidants based on flavonoids. In non-polar phases, the antioxidative activity of apigenin was increased by the electron-withdrawing groups, while it was reduced by the electron-donating groups. Contrary results occurred in the polar phase. The electronic effect of the substituents on BDE(4'-OH), BDE(5-OH), PA(4'-OH), and IP is mainly controlled by the resonance effect, while that on BDE(7-OH), PA(5-OH), and PA(7-OH) is governed by the field/inductive effect.
Keywords: Hammett sigma constants; apigenin; density functional theory; structure–antioxidant activity relationship; substituent effect.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Rhayem Y., Thérond P., Camont L., Couturier M., Beaudeux J.L., Legrand A., Jore D., Gardés-Albert M., Bonnefont-Rousselot D. Chain-breaking activity of resveratrol and piceatannol in a linoleate micellar model. Chem. Phys. Lipids. 2008;155:48–56. doi: 10.1016/j.chemphyslip.2008.06.001. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous