Targeting the Microenvironment in High Grade Serous Ovarian Cancer
- PMID: 30103384
- PMCID: PMC6115937
- DOI: 10.3390/cancers10080266
Targeting the Microenvironment in High Grade Serous Ovarian Cancer
Abstract
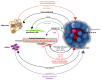
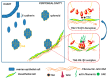
Cancer⁻stroma interactions play a key role in cancer progression and response to standard chemotherapy. Here, we provide a summary of the mechanisms by which the major cellular components of the ovarian cancer (OC) tumor microenvironment (TME) including cancer-associated fibroblasts (CAFs), myeloid, immune, endothelial, and mesothelial cells potentiate cancer progression. High-grade serous ovarian cancer (HGSOC) is characterized by a pro-inflammatory and angiogenic signature. This profile is correlated with clinical outcomes and can be a target for therapy. Accumulation of malignant ascites in the peritoneal cavity allows for secreted factors to fuel paracrine and autocrine circuits that augment cancer cell proliferation and invasiveness. Adhesion of cancer cells to the mesothelial matrix promotes peritoneal tumor dissemination and represents another attractive target to prevent metastasis. The immunosuppressed tumor milieu of HGSOC is permissive for tumor growth and can be modulated therapeutically. Results of emerging preclinical and clinical trials testing TME-modulating therapeutics for the treatment of OC are highlighted.
Keywords: angiogenesis; high-grade serous ovarian cancer; immune response; metastasis; therapeutic targeting strategies; tumor microenvironment.
Conflict of interest statement
D.M. received consulting honoraria from Roche. The other authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, and in the decision to publish the results.
Figures
References
-
- Hurteau J., Rodriguez G.C., Whitaker R.S., Shah S., Mills G., Bast R.C., Berchuck A. Transforming growth factor-beta inhibits proliferation of human ovarian cancer cells obtained from ascites. Cancer. 1994;74:93–99. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(19940701)74:1<93::AID-CNCR2820740117>3.0.CO;2-P. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

