Determinants of Behaviour Change in a Multi-Component Telemonitoring Intervention for Community-Dwelling Older Adults
- PMID: 30103399
- PMCID: PMC6115846
- DOI: 10.3390/nu10081062
Determinants of Behaviour Change in a Multi-Component Telemonitoring Intervention for Community-Dwelling Older Adults
Abstract
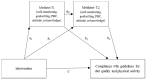
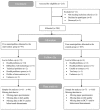
Optimal diet quality and physical activity levels are essential for healthy ageing. This study evaluated the effects of a multi-component telemonitoring intervention on behavioural determinants of diet quality and physical activity in older adults, and assessed the mediating role of these determinants and two behaviour change techniques in the intervention's effects. A non-randomised controlled design was used including 214 participants (average age 80 years) who were allocated to the intervention or control group based on municipality. The six-month intervention consisted of self-measurements of nutritional outcomes and physical activity, education, and follow-up by a nurse. The control group received regular care. Measurements took place at baseline, after 4.5 months and at the end of the study. The intervention increased self-monitoring and improved knowledge and perceived behavioural control for physical activity. Increased self-monitoring mediated the intervention's effect on diet quality, fruit intake, and saturated fatty acids intake. Improved knowledge mediated the effect on protein intake. Concluding, this intervention led to improvements in behavioural determinants of diet quality and physical activity. The role of the hypothesised mediators was limited. Insight into these mechanisms of impact provides directions for future development of nutritional eHealth interventions for older adults, in which self-monitoring may be a promising behaviour change technique. More research is necessary into how behaviour change is established in telemonitoring interventions for older adults.
Keywords: diet quality; lifestyle intervention; mechanisms of impact; mediation analyses; older adults; physical activity; telemonitoring.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, and in the decision to publish the results.
Figures
References
-
- Ocke M.C., Buurma-Rethans E.J.M., De Boer E.J., Wilson-van den Hooven C., Etemad-Ghameslou Z., Drijvers J.J.M.M., Van Rossum C.T.M. Diet of Community-Dwelling Older Adults: Dutch National Food Consumption Survey Older Adults 2010–2012. [(accessed on 8 August 2018)]; Available online: http://rivm.openrepository.com/rivm/handle/10029/305649.
-
- Ziylan C., Haveman-Nies A., Van Dongen E.J.I., Kremer S., De Groot C.P.G.M. Dutch Nutrition and Care Professionals’ Experiences with Undernutrition Awareness, Monitoring, and Treatment among Community-Dwelling Older Adults: A. Qualitative Study. BMC Nutr. 2015;1:38. doi: 10.1186/s40795-015-0034-6. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical