Effects of Carbon Source on TiC Particles' Distribution, Tensile, and Abrasive Wear Properties of In Situ TiC/Al-Cu Nanocomposites Prepared in the Al-Ti-C System
- PMID: 30103408
- PMCID: PMC6116243
- DOI: 10.3390/nano8080610
Effects of Carbon Source on TiC Particles' Distribution, Tensile, and Abrasive Wear Properties of In Situ TiC/Al-Cu Nanocomposites Prepared in the Al-Ti-C System
Abstract
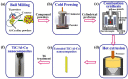
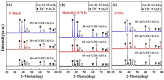
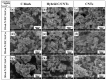
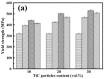
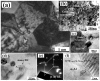
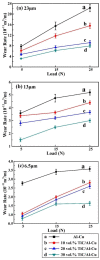
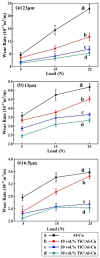
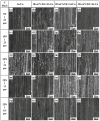
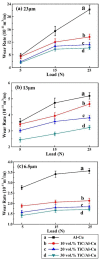
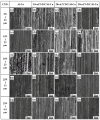
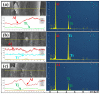
The in situ TiC/Al-Cu nanocomposites were fabricated in the Al-Ti-C reaction systems with various carbon sources by the combined method of combustion synthesis, hot pressing, and hot extrusion. The carbon sources used in this paper were the pure C black, hybrid carbon source (50 wt.% C black + 50 wt.% CNTs) and pure CNTs. The average sizes of nano-TiC particles range from 67 nm to 239 nm. The TiC/Al-Cu nanocomposites fabricated by the hybrid carbon source showed more homogenously distributed nano-TiC particles, higher tensile strength and hardness, and better abrasive wear resistance than those of the nanocomposites fabricated by pure C black and pure CNTs. As the nano-TiC particles content increased, the tensile strength, hardness, and the abrasive wear resistance of the nanocomposites increased. The 30 vol.% TiC/Al-Cu nanocomposite fabricated by the hybrid carbon source showed the highest yield strength (531 MPa), tensile strength (656 MPa), hardness (331.2 HV), and the best abrasive wear resistance.
Keywords: Al matrix nanocomposites; abrasive wear behaviors; in situ nano-TiC; tensile properties.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest regarding the publication of this paper.
Figures






References
-
- Zhao Y.F., Ma X., Chen H.W., Zhao X.J., Liu X.F. Preferred orientation and interfacial structure in extruded nano-Al3BC/6061Al. Mater. Des. 2017;131:23–31. doi: 10.1016/j.matdes.2017.05.088. - DOI
-
- Mathew J., Mandal A., Deepak Kumar S., Bajpai S., Chakraborty M., West G.D., Srirangam P. Effect of semi-solid forging on microstructure and mechanical properties of in-situ cast Al-Cu-TiB2 composites. J. Alloys Compd. 2017;712:460–467. doi: 10.1016/j.jallcom.2017.04.113. - DOI
-
- Selvakumar N., Sivaraj M., Muthuraman S. Microstructure characterization and thermal properties of Al-TiC sintered nano composites. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2016;107:625–632. doi: 10.1016/j.applthermaleng.2016.07.005. - DOI
-
- Ghasali E., Fazili A., Alizadeh M., Shirvanimoghaddam K., Ebadzadeh T. Evaluation of microstructure and mechanical properties of Al-TiC metal matrix composite prepared by conventional, microwave and spark plasma sintering methods. Materials. 2017;10:1255. doi: 10.3390/ma10111255. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

