Magnolol: A Neolignan from the Magnolia Family for the Prevention and Treatment of Cancer
- PMID: 30103472
- PMCID: PMC6121321
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms19082362
Magnolol: A Neolignan from the Magnolia Family for the Prevention and Treatment of Cancer
Abstract
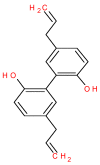
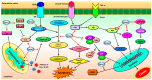
The past few decades have witnessed widespread research to challenge carcinogenesis; however, it remains one of the most important health concerns with the worst prognosis and diagnosis. Increasing lines of evidence clearly show that the rate of cancer incidence will increase in future and will create global havoc, designating it as an epidemic. Conventional chemotherapeutics and treatment with synthetic disciplines are often associated with adverse side effects and development of chemoresistance. Thus, discovering novel economic and patient friendly drugs that are safe and efficacious is warranted. Several natural compounds have proved their potential against this dreadful disease so far. Magnolol is a hydroxylated biphenyl isolated from the root and stem bark of Magnolia tree. Magnolol can efficiently prevent or inhibit the growth of various cancers originating from different organs such as brain, breast, cervical, colon, liver, lung, prostate, skin, etc. Considering these perspectives, the current review primarily focuses on the fascinating role of magnolol against various types of cancers, and the source and chemistry of magnolol and the molecular mechanism underlying the targets of magnolol are discussed. This review proposes magnolol as a suitable candidate that can be appropriately designed and established into a potent anti-cancer drug.
Keywords: cancer; chemoresistance; magnolol; molecular targets; phytochemicals.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

