Transcriptome Analysis of JA Signal Transduction, Transcription Factors, and Monoterpene Biosynthesis Pathway in Response to Methyl Jasmonate Elicitation in Mentha canadensis L
- PMID: 30103476
- PMCID: PMC6121529
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms19082364
Transcriptome Analysis of JA Signal Transduction, Transcription Factors, and Monoterpene Biosynthesis Pathway in Response to Methyl Jasmonate Elicitation in Mentha canadensis L
Abstract
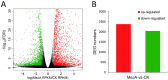
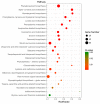
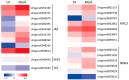
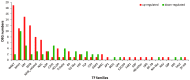
Mentha canadensis L. has important economic value for its abundance in essential oils. Menthol is the main component of M. canadensis essential oils, which is certainly the best-known monoterpene for its simple structure and wide applications. However, the regulation of menthol biosynthesis remains elusive in M. canadensis. In this study, transcriptome sequencing of M. canadensis with MeJA treatment was applied to illustrate the transcriptional regulation of plant secondary metabolites, especially menthol biosynthesis. Six sequencing libraries were constructed including three replicates for both control check (CK) and methyl jasmonate (MeJA) treatment and at least 8 Gb clean bases was produced for each library. After assembly, a total of 81,843 unigenes were obtained with an average length of 724 bp. Functional annotation indicated that 64.55% of unigenes could be annotated in at least one database. Additionally, 4430 differentially expressed genes (DEGs) with 2383 up-regulated and 2047 down-regulated transcripts were identified under MeJA treatment. Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) enrichment indicated that "Monoterpenoid biosynthesis" was one of the most significantly enriched pathways in metabolism. Subsequently, DEGs involved in JA signal transduction, transcription factors, and monoterpene biosynthesis were analyzed. 9 orthologous genes involved in menthol biosynthesis were also identified. This is the first report of a transcriptome study of M. canadensis and will facilitate the studies of monoterpene biosynthesis in the genus Mentha.
Keywords: JA signaling; Mentha canadensis L.; menthol biosynthesis; transcription factors; transcriptome sequencing.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Turner G.W., Croteau R. Organization of monoterpene biosynthesis in Mentha, immunocytochemical localizations of geranyl diphosphate synthase, limonene-6-hydroxylase, isopiperitenol dehydrogenase, and pulegone reductase. Plant Physiol. 2004;136:4215–4227. doi: 10.1104/pp.104.050229. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

