Modulation of Apoptosis by Cytotoxic Mediators and Cell-Survival Molecules in Sjögren's Syndrome
- PMID: 30103522
- PMCID: PMC6121505
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms19082369
Modulation of Apoptosis by Cytotoxic Mediators and Cell-Survival Molecules in Sjögren's Syndrome
Abstract
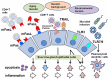
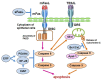
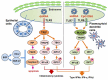
The pathogenesis of Sjögren's syndrome (SS) involves multiple factors including genetic background, cell death, and exocrine dysfunction. We here discuss apoptotic control in exocrine glands in SS by showing various pro- and anti-apoptotic pathways. Although the membrane-bound and soluble form of the Fas/Fas ligand system is a leading player with activation of the death domain and caspase 8/3 cleavage, the role of soluble Fas/FasL (including its polymorphism) in apoptosis is controversial. The tumor necrosis factor related apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL)-mediated apoptosis of salivary gland epithelial cells (SGECs) involves a mitochondrial pathway that includes caspase 9 cleavage. The involvement of innate immunity cells such as toll-like receptors (TLRs) has been investigated; TLR2-4 and TLR7-9 are associated with the induction of inflammation in exocrine glands of SS patients. TLR3 has the potential to induce the apoptosis of SS patients' SGECs. Linkage of epidermal growth factor (EGF) was shown in exocrine glands in SS, and it inhibited the Fas/FasL system with the help of cell-survival factors. TLR3 has dual actions to cause inflammation as well as apoptosis, which are inhibited by EGF. In conclusion, apoptosis in exocrine glands of SS patients is tightly controlled by balance of pro-apoptotic signals and growth factor.
Keywords: EGF; Fas; Sjögren’s syndrome; TLR; apoptosis; cell survival molecule; salivary gland epithelial cells.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The role of apoptosis in Sjögren's syndrome.Ann Med Interne (Paris). 1998 Feb;149(1):25-9. Ann Med Interne (Paris). 1998. PMID: 11490513 Review.
-
Analysis of the downstream mediators of toll-like receptor 3-induced apoptosis in labial salivary glands in patients with Sjögren's syndrome.Mod Rheumatol. 2016;26(1):99-104. doi: 10.3109/14397595.2015.1045256. Epub 2015 May 28. Mod Rheumatol. 2016. PMID: 25926385
-
Apoptosis in labial salivary glands from Sjögren's syndrome (SS) patients: comparison with human T lymphotropic virus-I (HTLV-I)-seronegative and -seropositive SS patients.Clin Exp Immunol. 1998 Oct;114(1):106-12. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2249.1998.00692.x. Clin Exp Immunol. 1998. PMID: 9764611 Free PMC article.
-
Induction of salivary gland epithelial cell injury in Sjogren's syndrome: in vitro assessment of T cell-derived cytokines and Fas protein expression.J Autoimmun. 2001 Sep;17(2):141-53. doi: 10.1006/jaut.2001.0524. J Autoimmun. 2001. PMID: 11591123
-
[Cell death of salivary gland epithelial cells and involvement of HTLV-I in Sjögren's syndrome].Nihon Rinsho Meneki Gakkai Kaishi. 2014;37(3):117-24. doi: 10.2177/jsci.37.117. Nihon Rinsho Meneki Gakkai Kaishi. 2014. PMID: 24974922 Review. Japanese.
Cited by
-
Molecular Mechanisms Linking Inflammation to Autoimmunity in Sjögren's Syndrome: Identification of New Targets.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Oct 30;23(21):13229. doi: 10.3390/ijms232113229. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36362017 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Role of Viral Infections in the Pathogenesis of Sjögren's Syndrome: Different Characteristics of Epstein-Barr Virus and HTLV-1.J Clin Med. 2020 May 13;9(5):1459. doi: 10.3390/jcm9051459. J Clin Med. 2020. PMID: 32414149 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Immune and non-immune mediators in the fibrosis pathogenesis of salivary gland in Sjögren's syndrome.Front Immunol. 2024 Oct 14;15:1421436. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1421436. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 39469708 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A comprehensive review of Sjögren's syndrome: Classification criteria, risk factors, and signaling pathways.Heliyon. 2024 Aug 15;10(17):e36220. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e36220. eCollection 2024 Sep 15. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 39286095 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Toll-like Receptor 7-Mediated Ro52 Antigen-Presenting Pathway in the Salivary Gland Epithelial Cells of Sjögren's Syndrome.J Clin Med. 2023 Jun 30;12(13):4423. doi: 10.3390/jcm12134423. J Clin Med. 2023. PMID: 37445456 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alani H., Henty J.R., Thompson N.L., Jury E., Ciurtin C. Systematic review and meta-analysis of the epidemiology of polyautoimmunity in Sjögren’s syndrome (secondary Sjögren’s syndrome) focusing on autoimmune rheumatic diseases. Scand. J. Rheumatol. 2018;47:141–154. doi: 10.1080/03009742.2017.1324909. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Ferro F., Marcucci E., Orlandi M., Baldini C., Bartoloni-Bocci E. One year in review 2017: Primary Sjögren’s syndrome. Clin. Exp. Rheumatol. 2017;35:179–191. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

