Mesenchymal stem cell transplantation improves chronic colitis-associated complications through inhibiting the activity of toll-like receptor-4 in mice
- PMID: 30103680
- PMCID: PMC6090774
- DOI: 10.1186/s12876-018-0850-7
Mesenchymal stem cell transplantation improves chronic colitis-associated complications through inhibiting the activity of toll-like receptor-4 in mice
Abstract
Background: A variety of extra-intestinal manifestations (EIMs), including hepatobiliary complications, are associated with inflammatory bowel disease (IBD). Mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) have been shown to play a potential role in the therapy of IBD. This study was designed to investigate the effect and mechanism of MSCs on chronic colitis-associated hepatobiliary complications using mouse chronic colitis models induced by dextran sulfate sodium (DSS).
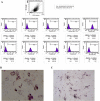
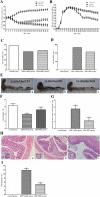
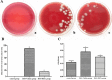
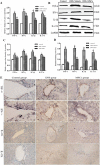
Methods: DSS-induced mouse chronic colitis models were established and treated with MSCs. Severity of colitis was evaluated by disease activity index (DAI), body weight (BW), colon length and histopathology. Serum lipopolysaccharide (LPS) levels were detected by limulus amebocyte lysate test (LAL-test). Histology and liver function of the mice were checked correspondingly. Serum LPS levels and bacterial translocation of mesenteric lymph nodes (MLN) were detected. Pro-inflammatory cytokines including tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α), interferon-γ (IFN-γ), interleukin-1β (IL-1β), interleukin-17A (IL-17A), Toll receptor 4 (TLR4), TNF receptor-associated factor 6 (TRAF6) and nuclear factor kappa B (NF-κB) were detected by immunohistochemical staining, western blot analysis and real-time PCR, respectively.
Results: The DSS-induced chronic colitis model was characterized by reduced BW, high DAI, worsened histologic inflammation, and high levels of LPS and E. coli. Liver histopathological lesions, impaired liver function, enhanced proteins and mRNA levels of TNF-α, IFN-γ, IL-1β, IL-17A, TLR4, TRAF6 and NF-κB were observed after DSS administration. MSCs transplantation markedly ameliorated the pathology of colon and liver by reduction of LPS levels and proteins and mRNA expressions of TNF-α, IFN-γ, IL-1β, IL-17A, TLR4, TRAF6 and NF-κB.
Conclusions: MSCs can improve chronic colitis-associated hepatobiliary complications, probably by inhibition of enterogenous endotoxemia and hepatic inflammation through LPS/TLR4 pathway. MSCs may represent a novel therapeutic approach for chronic colitis-associated hepatobiliary complications.
Keywords: Chronic colitis; Hepatobiliary complications; Lipopolysaccharide; Mesenchymal stem cells; Toll receptor 4.
Conflict of interest statement
Not applicable.
The authors declare that they had no competing interests.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Figures



References
-
- Yang X, Meng J. Hepatopancreatobiliary complications among patients with inflammatory bowel disease. Chin Gen Pract. 2011;14:2398–2401.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

