A Digital RNA Signature of Circulating Tumor Cells Predicting Early Therapeutic Response in Localized and Metastatic Breast Cancer
- PMID: 30104333
- PMCID: PMC6170694
- DOI: 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-18-0432
A Digital RNA Signature of Circulating Tumor Cells Predicting Early Therapeutic Response in Localized and Metastatic Breast Cancer
Abstract
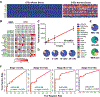
The multiplicity of new therapies for breast cancer presents a challenge for treatment selection. We describe a 17-gene digital signature of breast circulating tumor cell (CTC)-derived transcripts enriched from blood, enabling high-sensitivity early monitoring of response. In a prospective cohort of localized breast cancer, an elevated CTC score after three cycles of neoadjuvant therapy is associated with residual disease at surgery (P = 0.047). In a second prospective cohort with metastatic breast cancer, baseline CTC score correlates with overall survival (P = 0.02), as does persistent CTC signal after 4 weeks of treatment (P = 0.01). In the subset with estrogen receptor (ER)-positive disease, failure to suppress ER signaling within CTCs after 3 weeks of endocrine therapy predicts early progression (P = 0.008). Drug-refractory ER signaling within CTCs overlaps partially with presence of ESR1 mutations, pointing to diverse mechanisms of acquired endocrine drug resistance. Thus, CTC-derived digital RNA signatures enable noninvasive pharmacodynamic measurements to inform therapy in breast cancer.Significance: Digital analysis of RNA from CTCs interrogates treatment responses of both localized and metastatic breast cancer. Quantifying CTC-derived ER signaling during treatment identifies patients failing to respond to ER suppression despite having functional ESR1. Thus, noninvasive scoring of CTC-RNA signatures may help guide therapeutic choices in localized and advanced breast cancer. Cancer Discov; 8(10); 1286-99. ©2018 AACR. This article is highlighted in the In This Issue feature, p. 1195.
©2018 American Association for Cancer Research.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures



References
-
- O’leary B, Finn RS, Turner NC. Treating cancer with selective CDK4/6 inhibitors. Nature Reviews Clinical Oncology. 2016;13: 417–430. - PubMed
-
- Hortobagyi GN, Stemmer SM, Burris HA, et al. Ribociclib as first-line therapy for HR-positive, advanced breast cancer. New England Journal of Medicine. 2016;375: 1738–1748. - PubMed
-
- Turner NC, Ro J, André F, et al. Palbociclib in hormone-receptor–positive advanced breast cancer. New England Journal of Medicine. 2015;373: 209–219. - PubMed
-
- Hart CD, Migliaccio I, Malorni L, Guarducci C, Biganzoli L, Di Leo A. Challenges in the management of advanced, ER-positive, HER2-negative breast cancer. Nature Reviews Clinical Oncology. 2015;12: 541–552. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

